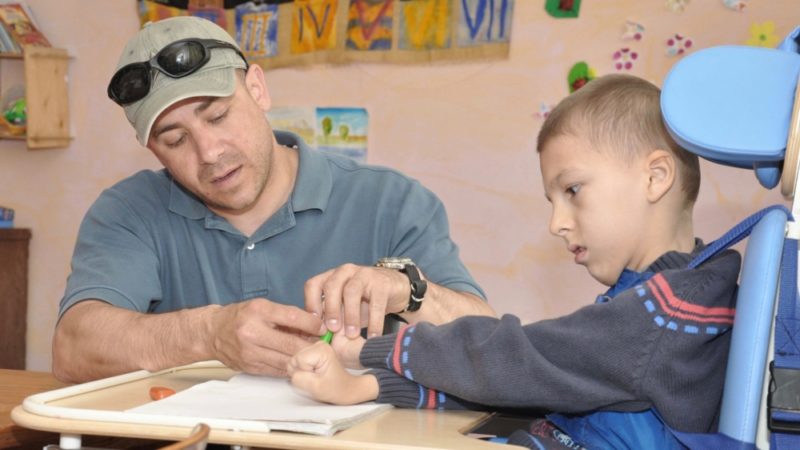
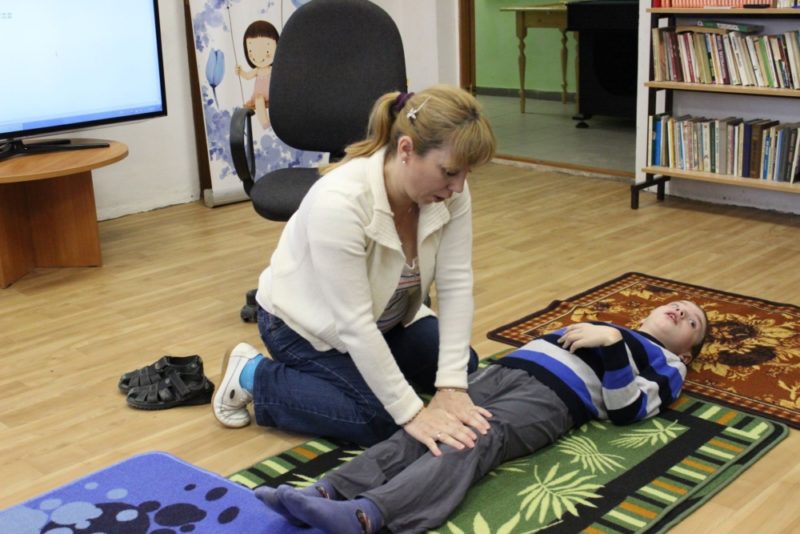
Cerebral palsy is not a specific disease, but a combination of various symptoms. The disease can manifest itself both in mental and motor disorders, it always has only a chronic course, does not progress. The causes of cerebral palsy are damage to areas of the brain. Pathology can be caused by hypoxia, trauma or infection. It is impossible to completely get rid of it, however, after a good rehabilitation, the patient's condition improves significantly.
Material Content:
What is cerebral palsy?
Cerebral palsy is a multifaceted disease that manifests itself in various disorders of motor activity and mental abilities, epileptic seizures. It occurs due to damage to brain structures during gestation, during childbirth or in the first weeks of life.
Since each organ site is responsible for its functions, the symptoms of the disease are very different.
Muscular paralysis does not progress throughout life, but it is not always possible to completely get rid of it. Even with constant treatment, sick children receive disabilities.
The difference between cerebral palsy and pathologies with similar symptom complexes is a clear damage to the structures of the brain, which does not extend to neighboring tissues. The frequency of paralysis is almost 2 cases per 1000 newborns.In boys, the lesion is somewhat more common than in young women.
Classification of forms
Forms of cerebral palsy depend on the clinical picture and localization of brain damage.
In total, 5 types of disease are distinguished:
- spastic diplegia (the second name is Little's disease);
- hemiplegia;
- double hemiplegia;
- hyperkinetic paralysis;
- atonic-astatic cerebral palsy.
A mixed form of pathology is also found, which is characterized by the presence of different symptom complexes. It develops rarely, about 1% of all cases, and has an unfavorable course.
- Spastic diplegia is the most common type of cerebral palsy, which is diagnosed in almost half of patients. More at risk of such damage are premature babies. The clinical picture becomes apparent in 10-12 months - paresis of the upper and lower extremities occurs, and the legs suffer more. Children are constantly in the same position - the arms are bent and pressed to the chest, and the legs are straight, tightly compressed or crossed. In the process of further growth, deformity of the feet develops. Intelligence, learning ability and memory in these children are reduced, the work of speech and hearing aids is impaired. Convulsive seizures occur much less frequently compared to other forms of cerebral palsy.
- Hemiplegia is diagnosed in more than 30% of diseases. It is characterized by a unilateral lesion of the limbs, with a large paresis of the arm. You can identify this type immediately after the birth of the child. Intelligence is also reduced, at an older age it is difficult for the baby to pronounce words. In half of the patients, epileptic seizures, convulsions are recorded, their frequency directly depends on the severity of the disease.
- The most severe form of cerebral palsy is double hemiplegia, which occurs in 2 to 3% of small patients. The reason for its appearance is prolonged hypoxia during childbirth, which damages a significant area of the brain. Symptoms of the disease are noticeable already from the first months of the baby’s life: arms and legs are in constant tone, pressed to the body, the child is in a state of apathy or euphoria, convulsive seizures often occur. Older children are poorly trained, unable to remember many words, practically do not speak.
- With the hyperkinetic form, constant involuntary movements of different muscle groups occur - on the face, arms, neck, legs. The activity and range of action increases with nervous excitement. The disease begins to appear in the second year of life, damage does not affect the intellectual abilities of the child, there is no developmental delay. Often patients successfully graduate from high school and enroll in universities.
- In children suffering from atonic-astatic cerebral palsy, pronounced muscle hypotension is observed, that is, constant relaxation. Such patients sit down late, it is difficult for them to stand and walk. There is a lack of coordination, tremors of the limbs and head are observed. Intelligence is slightly reduced.
During cerebral palsy, three stages are distinguished:
- early - symptoms do not appear at all or they are invisible;
- initial chronic-residual - the flowering of the clinical picture;
- final residual - new symptoms cease to appear, the disease stops at the same level of development.
There are two kinds of final stages. With one child, one can teach self-care skills; he can live a practically full life. In the second, the patient cannot be trained due to serious mental or motor impairment.
The prognosis of the disease depends on the type of lesion and the quality of rehabilitation. There were cases of almost complete cure, when cerebral palsy made itself felt only with minor motor dysfunctions.
Causes of cerebral palsy in newborns
The causes of cerebral palsy in children are factors that adversely affect the development of the brain or damage its structure.
The development of the disease can lead to:
- failure in cell division during intrauterine organ laying;
- severe fetal hypoxia during gestation;
- acute lack of oxygen in the body;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- toxic effects on the pregnant woman (lead poisoning, taking teratogenic drugs);
- blood rhesus conflict;
- head injuries.
Often, cerebral palsy begins to develop during childbirth due to tight entanglement of the umbilical cord, placental abruption, deep prematurity of the baby, medical errors.
Is it possible to detect during pregnancy
Unfortunately, the diagnosis of cerebral palsy during pregnancy is impossible. Even after the birth of the baby, it is not always possible to determine the presence of the disease, for most patients the diagnosis is made in the second half of life.
Cerebral palsy can also develop in a healthy newborn due to trauma during or after childbirth, due to careless handling of medical staff or the mother. The baby's brain is very sensitive to physical and chemical damage, oxygen starvation.
Hereditary predisposition
Cerebral palsy in newborns is not a genetic pathology, therefore it can not be inherited. At the gene level, only the characteristics of each organism are transmitted that can affect the course of the disease, for example, endurance and resistance of the nervous system.
In patients with cerebral palsy, sometimes deviations are inherited, which are inherited, such as:
- blastomatosis;
- poor blood circulation in the vessels of the brain;
- bouts of hysteria;
- episodes of epileptic seizures;
- splitting of the spine and spinal cord.
Symptoms of Cerebral Palsy
The main symptoms of cerebral palsy are various disorders of motor activity. Sick children hold their heads poorly, learn to roll over late, sit, move around. They have congenital reflexes for a long time. About 30% of patients experience cramps, with the first episodes appearing after 1 to 2 years.
It is difficult to diagnose cerebral palsy during infancy, but there are early signs that should alert parents:
- lack of reaction to a loud sound in a month-old baby;
- at 4 - 5 months, the baby does not turn his head in response to stimuli, does not pull the handles to an interesting subject;
- at 7-8 months, the child does not sit without support, but at 12 does not walk;
- the baby has only one hand active - he eats, plays, gestures with it;
- the presence of strabismus;
- inhibited or, conversely, slow motion;
- the appearance of seizures.
The presence of at least one of the above signs should be the reason for going to the doctor. Successful treatment for cerebral palsy is early diagnosis and the beginning of rehabilitation.
Diagnostic measures
To diagnose cerebral palsy, a set of symptoms is enough for an experienced doctor. If the family has already had cases of such diseases, paralysis progresses, or the patient has many other abnormalities, it is necessary to conduct differential diagnosis with genetic pathologies.
You can confirm the diagnosis of cerebral palsy with MRI. The images will show structural changes in the brain - atrophy, decreased white matter density and pseudoporencephaly.