An atrial septal defect or ASD is a disease considered to be one of the most common heart defects. Symptoms, the course and prognosis may vary depending on the severity and conditions of the disease. In this article, we will analyze in detail the prerequisites for the occurrence of ASD, symptoms and treatment methods.
Material Content:
Causes of atrial septal defect
The human heart is divided into four chambers - two atria and the same number of ventricles. The chambers are interconnected by valves that determine the regulation of blood flow in the heart chambers. Accordingly, blood can flow from the atria to the ventricles. But blood from different atria should not be in contact with each other.
With a normal heart structure, both atria are separated by a septum. With intrauterine development, as well as the first months after birth, the presence of an opening in the atrial septum is a natural phenomenon. Normally, it disappears in the period up to one year. Sometimes the hole remains later, then we are talking about DMPP.
The occurrence of this defect occurs due to the fact that in the embryonic period there is no full-fledged development of the septum between the right and left atria.The influence factors may include the influence of harmful environmental influences, infection of the mother and a number of other reasons.
It is noted that the risk of an atrial septal defect in children is increased if similar malformations also occurred in relatives. Also affected by the mother during the period of bearing the infection, rubella, herpes, chickenpox and others affect the development of ASD. In addition, some medications taken when carrying a child, alcohol and narcotic substances, radiation and pathologies of the endocrine system may affect.
Symptoms and signs of pathology in children and adults
Symptoms of ASD may vary depending on the severity of the disease.
In mild cases, the absence of certain manifestations is observed, and the patient learns about the pathology only on a planned examination of the heart. The atrial septal defect in newborns usually does not manifest itself, especially in cases where the opening does not reach a large size.
As a rule, the main symptomatology manifests itself by about thirty years.
The following symptoms may indicate the development of ASD:
- frequent shortness of breath, provided that the load on the body is not carried out;
- the appearance of edema, mainly in the lower parts of the body;
- a feeling of loss of strength and severe fatigue;
- blanching of the skin and mucous membranes, cyanosis;
- disturbed heart rhythm;
- frequent diseases of the respiratory system.
With a pronounced violation and the absence of hemodynamic compensation, symptoms begin to manifest at an early age. It should be noted that this congenital heart disease can cause a delay in physical development in children, tachycardia and rapid respiratory diseases, therefore it is necessary to timely diagnose and begin treatment.
Features of congenital malformation
With a defect in the atrial septum, blood circulation is disturbed - an increased load is placed on the heart associated with moving the blood in an unnecessary direction. At a young age, the body can provide compensation for this condition, but the older a person becomes, the greater the risk of complications and heart failure.
In addition, the blood from the arteries and veins is mixed, and this can be fraught with the appearance of blood clots, which are present in the venous blood, flow to the organs. As a result, there is a risk of strokes and heart attacks that occur due to the fact that the lumen of the vessel is blocked. At risk are patients suffering from atherosclerosis.
The amount of ejection of blood directly depends on the diameter of the hole. Based on this, the severity of the patient's condition is determined.
In the absence of competent and adequate treatment, complications can occur, such as serious heart rhythm disturbances, increased likelihood of strokes, the risk of pulmonary hypertension, the possibility of pneumonia due to blood oversaturation of the pulmonary vessels.
Classification of ASD
This heart disease can be classified according to various signs. In separate groups, primary and secondary cases of ASD are distinguished.
The first can include those cases in which the violation is localized in the area of the primary septum. Accordingly, communication between the two atria is maintained. In size, such a defect is usually larger, can reach 3 cm, and is located most often along the lower edge of the septum.
With a secondary defect of the atrial septum, we are talking about violations of the development of the secondary septum. In this case, the diameter of the hole is less, reaches about 1 cm, is localized closer to the middle part of the septum.
In severe cases, such a violation is recorded as the complete absence of a septum between the atria, then they talk about a three-chambered heart.
Combined pathologies are distinguished into a separate category when there are signs of both primary and secondary defects.Most often, this condition is diagnosed together with other congenital heart defects.
And sometimes a diagnosis such as an open oval window is made. It cannot be fully considered a complete defect of the septum, as it is expressed in the weak development of the oval valve directly. This is a less serious condition than other cases of ASD, but it also requires timely intervention by a cardiologist.
Diagnostic measures
When the patient contacts the cardiologist with the appropriate complaints, a detailed clinical picture and anamnesis are collected, after which a set of diagnostic procedures is prescribed.
At the initial diagnosis, the doctor draws attention to the characteristic systolic murmur during auscultation of the heart. Usually, after this, echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) is prescribed - it is considered the most informative diagnostic tool for identifying an atrial septal defect. You can detect the presence and exact location of the hole, get an idea of the size of the chambers of the heart.
An X-ray is also taken to get an idea of the size and shape of the heart, an ECG to find out what kind of heart rhythm disturbances are present, as well as angiography, which shows the exact pattern of blood flow.
A detailed picture of heart damage is shown by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Disease treatment
Previously, open heart surgery was considered the only way to cure an atrial septal defect. Now there are more opportunities for medical and rehabilitation measures.
Surgical method
In the traditional method of performing surgical intervention, a chest incision is made to gain access to the heart, after which suturing or placing the flap on the septum is performed. There is a more gentle method - then the incision does not exceed 5 cm, and the period of postoperative recovery is reduced.
The method by which the operation will be performed is chosen by the cardiac surgeon, depending on the severity of the patient's condition and associated pathologies.
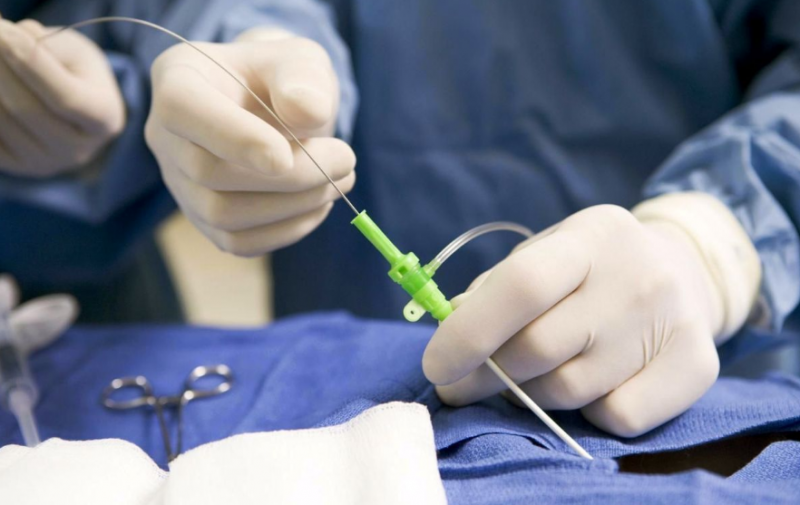
Endovascular method
One of the least invasive (traumatic) methods for eliminating a defect. Endovascular closure of the opening is performed by introducing a system of catheters into the femoral vein, with the help of which a special device, the occluder, is used to eliminate the hole.
During the procedure, the patient is controlled by radiography. At the same time, all the vital functions of the body are monitored without interruption.
The procedure is performed under general or local anesthesia - depending on the relevant indications. The catheter system and the occluder itself are selected for each patient individually, taking into account the characteristics of the violation. The entire procedure rarely lasts longer than one hour, the rehabilitation period is about a month and may be accompanied by shortness of breath or pain in the chest. In the event of the appearance of such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor in order to identify possible complications in time.
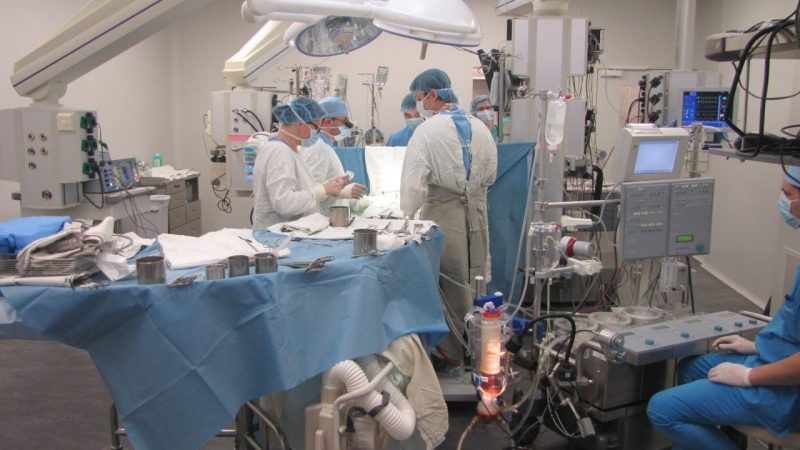
Cardiopulmonary bypass surgery
During the operation in case of ASD, according to this technique, an incision is made on the sternum in order to gain access to the heart, the patient is connected to a cardiopulmonary bypass system. And the heart itself is temporarily excluded from the circle of blood circulation. During this period of time, a patch is applied to the hole or it is completely sutured.
Then the heart is connected back, stitching is performed.
Rehabilitation period
The correct conduct of the recovery period after surgery is an important factor for the onset of recovery.
After performing surgery on an open heart, a bandage is prescribed in order to prevent the seam from diverging.
At first, before the order of the attending physician, a strict bed rest is required, then moving around the ward is allowed. It is unacceptable to remain motionless if there is no serious reason - activity strengthens the heart, increases ventilation of the lungs. The loads are increased gradually, reaching the level of activity that was before the disease will turn out no earlier than in 2-3 months.
Two weeks after surgery, body hygiene is carried out with a damp sponge, baths are prohibited. After healing, you can begin to take a warm, sedentary shower.
All recommendations that the doctor will give after discharge from the hospital should be carefully followed. Medications are taken at a strictly scheduled time, only as directed by a doctor.
It is necessary to observe a diet: food should be light, nutritious and containing the required number of calories. The restrictions that appear in the diet will need to be fulfilled all my life. This mainly concerns the restriction of salt, fats and excessively high-calorie foods.
Alcohol, tobacco, fatty pastries, pickled and smoked products, fatty meats are completely excluded.
Products leading to atherosclerosis (primarily for foods rich in fats) should be limited as much as possible so as not to cause vascular problems and obesity.
It is necessary to practice physical activity in a moderate mode. It is better to start with short walks, the first time to avoid stairs and any increased activity. It should be increased gradually after surgery in case of ASD, without overloading, but without avoiding movement. An ideal option would be to coordinate therapeutic exercises with your doctor.
At least two months will be required to remain under the supervision of a cardiologist. He corrects the diet and load, prescribes the necessary drugs. After the body recovers, functional testing is carried out, which will show a willingness to increase the load.
It is also important to avoid stressful situations and nervous overload. Relatives of the patient should be careful - nervous strain will give a strong load, which can cause complications.
Predictions for the recovery of children and adults
The prognosis for an atrial septal defect may depend on many factors, including the size of the opening, the presence of concomitant defects and complications, the timeliness of treatment started, age, and so on.
Hemodynamically insignificant deviations may not even require treatment - only a regular examination by a cardiologist will be required to exclude the progression of the pathology.
The prognosis worsens if the opening reaches such a size that leads to a mixture of arterial and venous blood. In this case, a favorable outcome depends on a timely operation, otherwise the situation may worsen.
Modern technology allows an intervention with minimal risk, however, it must be remembered that this is a heart operation. In this connection, there is a risk of complications even with a favorable course of treatment. Overall, survival during surgery is approximately 98%.
Late treatment and untimely diagnosis may adversely affect quality and life expectancy. In severe cases, this leads to disability after 30 years.