An important fluid in the human body is the tear. Its functionality can hardly be overestimated - tears moving along the nasolacrimal canal prevent the cornea from drying out. But an insidious disease - dacryocystitis sometimes interferes with the coordinated work of the tear ducts.
Material Content:
What is dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is called inflammation of the lacrimal sac, manifested in the closure of the nasolacrimal duct. Tears are not transported to the nasal cavity and accumulate in the bag, and he gradually overflows. The secreted secret becomes opaque, mucopurulent. The approaching tears do not have access to the lacrimal sac, the patient begins lacrimation.
Causes of occurrence
Dacryocystitis is provoked by obstruction of the nasolacrimal canal. The course of the disease varies depending on the age category of patients. So, in newborns, the disease is often provoked by an undissolved gelatinous plug or by features of the tear ducts.
Dacryocystitis in adults is provoked by a number of reasons:
- sinusitis, rhinitis;
- polyps of the nasal cavity;
- ARVI and so on.
Also associated with the development of dacryocystitis are nasal fractures, problems with adenoids, eyelid injuries.
Did you know? Dacryocystitis is due to a genetic predisposition to the formation of a cork, blocking the nasolacrimal duct.
Types of disease
Dacryocystitis of adults and newborns is isolated. These species require a fundamentally different therapeutic approach. Pathology in newborns often does not need treatment and passes on its own.Dacryocystitis in adults does not disappear itself, so patients are advised to visit an ophthalmologist and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Doctors distinguish 4 forms of dacryocystitis:
- Catarrhal. It is monitored at the beginning of the disease, its symptoms are eliminated more easily than in other forms.
- Stenosing. The nasolacrimal canal is noticeably narrowed, tears gradually accumulate in the corresponding “reservoir”.
- Empyema. The tearful bag is filled with pus. Immediate medical attention is indicated.
- Phlegmon. The most dangerous stage - pus is able to spread without regard to the boundaries of the corresponding channel.
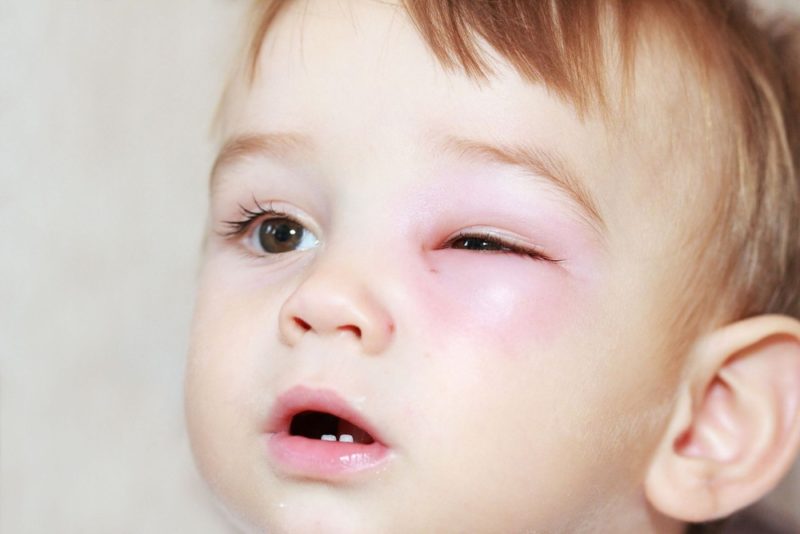
Dacryocystitis is divided into acute and chronic. The latter is marked by lacrimation, accumulation of pus in the corners of the eyes, swelling of the lacrimal sac. Acute dacryocystitis is monitored in edema of the eyelids, redness of the lacrimal sac, and so on.
Symptoms and signs in children and adults
The main signs of the disease are continuous lacrimation, pus emanating from the eyes, the organ of vision often swells.
Additional symptoms of dacryocystitis:
- narrowing of the palpebral fissure;
- inflammation in the lunar fold, eyelids;
- thinning of the skin lining the lacrimal sac.
Symptoms vary depending on the age of the patient. The main symptoms of the disease are monitored in children in the first day of their life. The nasolacrimal canals of newborns are covered with a film torn after the birth of the baby. The lacrimal apparatus begins to work, but if the film does not tear, the tears do not go away, and dacryocystitis begins. This condition can pass on its own after a few months or require medical attention.
In infants, the disease manifests itself in a number of signs:
- dried crusts in the corners of the eye;
- incessant tearing;
- runny nose;
- redness of the eyes;
- oozing pus from the lacrimal sac (monitored by pressure).
Often, dacryocystitis completely disappears after about 6 months of life, with a maximum of one year.
Diagnostic Methods
The main methods for diagnosing dacryocystitis include:
- Blood analysis. In the presence of an eye disease, leukocytosis is monitored in the blood.
- Sonography. It is used infrequently, it helps to track stasis and tumors of the lacrimal sac.
- Probing of the lacrimal passages. It is used not only for medical, but also for diagnostic purposes to assess channel patency.
- CT Helps track the presence of various neoplasms or developed changes in the organ of vision.
- Nasal endoscopy Helps identify the pathology of the nasal concha.
Additions to the diagnosis are dacryocystography and dacryoscintigraphy. They allow you to identify abnormalities of the tear system.
Treatment for inflammation of the lacrimal sac
Treatment of dacryocystitis in adults and children should be carried out in a hospital under the supervision of physicians.
Combined therapy includes:
- Drug treatment. Acute dacryocystitis is eliminated by anti-inflammatory drugs: "Paracetamol", "Ketorol" and so on. These medicines are in tablet form or in the form of eye drops. Another component of drug treatment is considered antibacterial ointments (Erythromycin, Tetracycline, etc.).
- Physiotherapy. Enhances the effect of medicines and prevents complications. At the beginning of the disease, dry heat and UHF therapy are used. These procedures help stimulate the immune system, and are recommended for adults and children from 6 years old. Physiotherapy procedures are recommended by a specialist only for emergency cases to newborn patients and preschool children.
- Surgery. It is prescribed if drug therapy has not yielded results.
There are 2 main operational methods for solving the problems of the nasolacrimal canal:
- Dacryocystorhinostomy. During the intervention, a new channel is formed in the gap between the nasal cavity and the lacrimal sac. An endoscopic intervention technique helps to avoid facial cosmetic defects.
- Sounding.The specialist instills an injured eye with an anesthetic and uses 2 probes: Siechel (expansion of the ducts) and Bowman (cleaning the channels, eliminating the plug).
By the way. In some cases, medical leeches are used to treat dacryocystitis. Such treatment, of course, is not shown to everyone. However, often it is hirudotherapy that is suitable for eliminating the symptoms of an eye disease in pregnant women, due to the restriction of the use of future drugs by future mothers. The exact number of sessions is determined by the doctor, on average, 3-4 procedures are necessary.
Treatment of dacryocystitis in newborns involves 2 steps:
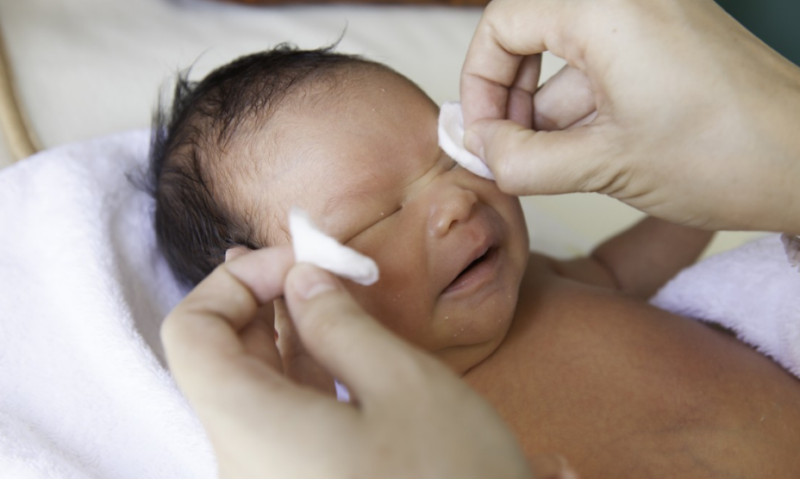
- Massage of the lacrimal canal. Often the manipulation of the newborn is carried out by the mother, making movements around the lacrimal sac.
- The use of antibacterial drops (tetracycline, chloramphenicol). It is carried out after massage. The duration of such therapy is 14 days. As an addition to drug therapy, it is permissible to use folk remedies for the treatment of eye pathologies. So, compresses from tea bags and a decoction of dill, as well as the use of drops of Kalanchoe, are considered effective in eliminating purulent discharge.
Tip. It is considered important to rinse the eyes and remove accumulated pus. Neglect of this recommendation is fraught with the development of conjunctivitis.
It is best to carry out the elimination of furatsilina separated by a solution (1 tablet per 200 ml of boiling water). The cotton soaked in the resulting solution cleanses the eye along the route from the temple to the nose.
Usually, following these recommendations, the symptoms of dacryocystitis in children disappear.
On a note. How to track that the applied therapy of dacryocystitis was successful? 2 main factors will indicate this: the absence of lacrimation and pus secreted from the eyes.
How to massage
Massage with dacryocystitis in newborns is part of the general treatment of eye ailment. The lacrimal sac is easy to feel by examining the inner eye angle - it is tracked through the skin in the nose bridge.
The procedure will be more effective if you consider several recommendations:
- Wash hands and cut nails before massage. The extremities are warmed up, otherwise there is a great risk of allowing the channel to become cold.
- The organs of vision are wiped with chamomile broth / disinfectant solution.
- The area between the eye and nose is well massaged, along the way, attention is paid to movements along the nose.
- The pressure should be palpable, but not excessive.
Such manipulation is carried out three times a day, promotes the breakdown of the gelatinous plug and removes pus out. The latter is removed with a cotton pad moistened with chamomile broth.
Possible complications
Acute dacryocystitis is a dangerous condition that can provoke the following complications:
- abscess of the lacrimal sac;
- meningitis;
- sepsis.
The main danger of the disease is the risk of further inflammation of nearby ENT organs or the brain. Complications of dacryocystitis can lead to disability, in extreme situations - to death.
Note. About 15% of people exposed to dacryocystitis have tear duct stones. Interestingly, in those who have a history of acute form of the disease, the risk of stone formation is higher than in patients prone to chronic dacryocystitis.
Prevention
You can avoid dacryocystitis by resorting to a number of preventive measures:
- prevention of eye injuries;
- timely treatment of nose diseases;
- observing the rules of eye hygiene.
If a foreign body enters the eye, remove it with extreme care and disinfect the eye. It is often impossible to carry out such a manipulation yourself, therefore, you should contact a specialist for help.
Dacryocystitis is often observed in infants due to the structural features of their organs of vision. The course of the disease in children is easier than in adults. In young patients, the pathology often goes away without medical intervention, but adults are shown special therapy.