Children's cough is a frequent and, at first glance, quite harmless phenomenon. However, even if this symptom does not indicate a dangerous disease, it alone can lead to complications. Therefore, it is important for parents to know how to treat a child's cough quickly and effectively.
Material Content:
The main causes of coughing in a child
A cough in a child appears due to irritation of receptors located in the tissues of the respiratory tract. The main goal of a cough is to cleanse the latter of mucus and foreign bodies that impede normal breathing.
Among the factors provoking this symptom, the following groups can be distinguished:
- mechanical (foreign body ingestion, sputum discharge in inflammatory diseases);
- allergic (irritation of the mucous membrane with an allergen);
- thermal (irritating effect of high or low temperatures);
- chemical (irritation of the mucosa by vapors of chemicals).
Sometimes coughing in children can be a kind of reaction to stress. In this case, it is not accompanied by sputum discharge and other symptoms and disappears on its own after eliminating the factor that takes the child out of psychological balance.
What diseases indicates
There are two types of cough: productive (wet, accompanied by discharge of sputum) and unproductive (dry). A dry cough often appears at the very beginning of an infectious disease, and then becomes wet, as the pathology develops. In addition, there is such a thing as a dry residual cough, which is not a manifestation of the disease and is observed within 1 to 3 weeks after completion of treatment.
Most often, cough in children accompanies the following diseases:
- ARVI;
- bronchitis;
- laryngitis;
- tracheitis;
- tonsillitis;
- allergies.
A prolonged paroxysmal cough may be a sign of more formidable diseases, including pneumonia, whooping cough, bronchial asthma, pulmonary tuberculosis. Therefore, it is very important in the development of this symptom in a child to consult a doctor on time.
In some situations, an unproductive cough without fever may indicate stomach diseases, in which the contents of the organ are thrown into the esophagus and irritate the mucous membrane of the throat and nasopharynx.
Diagnostic measures
It is not difficult to distinguish a dry cough from a wet one on its own. The first occurs without sputum discharge, has a “barking” sound and does not bring relief after an attack. The second has a peculiar, "wheezing" sound, and at the end of the attack it is accompanied by the release of sputum.
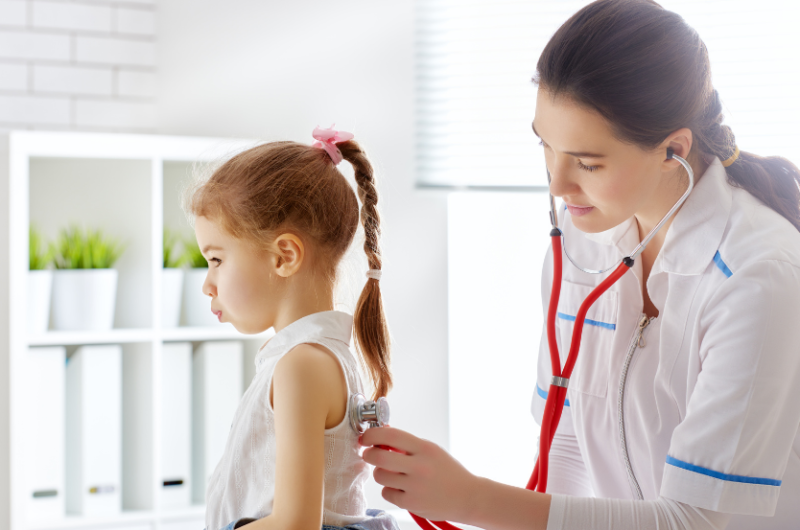
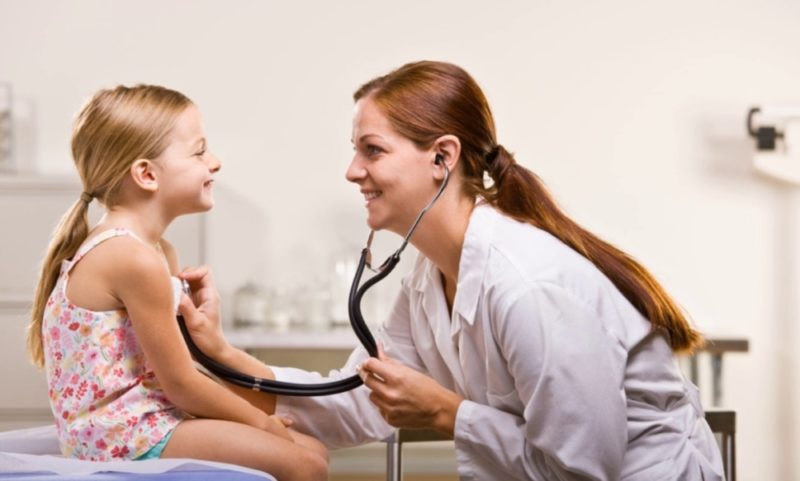
Before starting treatment for cough, it is necessary to determine its origin. A pediatrician should do this. The first stage of the examination is examining the child, collecting information about the nature and characteristics of the cough, listening to wheezing and other sounds characteristic of the pathology during breathing. They do this with the help of a well-known device - a stethoscope.
Also, a specialist will examine the throat, check whether the local lymph nodes are enlarged. Depending on the presence or absence of other symptoms (fever, malaise, etc.), the pediatrician can additionally prescribe a general blood test and analysis of sputum discharge, in rare cases, according to strict indications - radiological research methods.
If necessary, the doctor can refer the small patient for a consultation with narrow specialists: otolaryngologist, infectious disease specialist, allergist and others.
How to treat different forms of cough in children
Self-treatment of cough in children, without finding out the cause of the symptom, increases the risk of complications. It is especially important to consult a pediatrician if the child coughs heavily for a long time.
Medications
To cure a cough, the cause of its appearance should be eliminated.
Depending on the pathology that caused this symptom, the following groups of drugs can be prescribed:
- antibacterial agents (suspensions and tablets with amoxicillin and other broad-spectrum agents);
- antiviral (syrups, tablets, suppositories with antiviral and immunomodulatory effects);
- antihistamines (solutions and tablets with anti-allergic effect).
Antihistamines and antibiotics for the treatment of ailments accompanied by cough are used in children exclusively for the doctor's prescription. Unreasonable intake of these drugs can significantly worsen the course of the disease.
If the cough is of an infectious origin and is accompanied by a deterioration in overall well-being and high fever, painkillers and antipyretic drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are prescribed for the small patient. Most often in this case, suppositories and syrups with paracetamol and ibuprofen are used.
The choice of drugs for treating cough is determined by its type.
If a non-productive cough does not go wet for a long time, antitussive drugs are used:
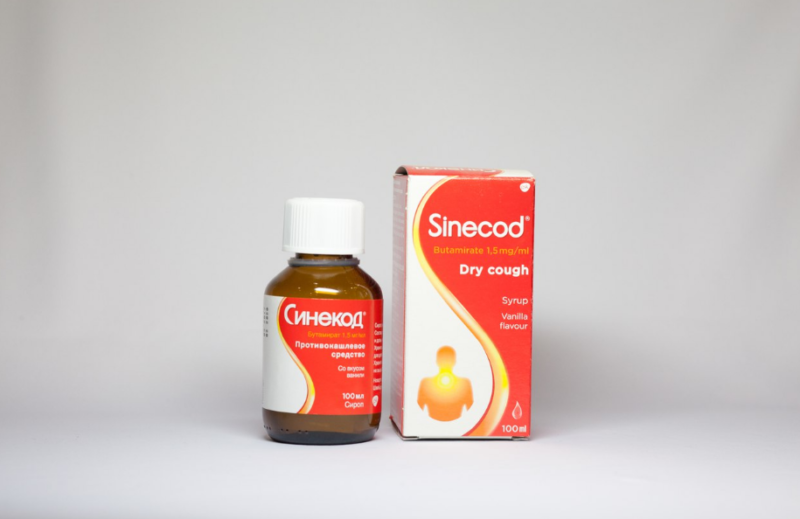
- butamirate ("Sinecode", "Omnitus");
- glaucin ("Broncholitin");
- prenoxodiazine (with caution).
These drugs act on the cough center or block the mucosal receptors of the respiratory tract.
Also, when coughing without sputum, medicines based on medicinal plants (“Herbion with plantain”, herbal preparations) and combined products containing not only antitussive, but also expectorant or anti-inflammatory components (“Stoptussin”, “Erespal”) can be prescribed.
For the treatment of wet coughs, preparations containing expectorants or mucolytics are used:
- Ambroxol (Lazolvan, Ambrobene);
- acetylcysteine (“ACC”, “Fluimucil”)
- bromhexine;
- expectorant preparations of plant origin (licorice root syrup, mucaltin, "Herbion with primrose", expectorant herbal preparations).
Ambroxol is often used for inhalation using a special device - a nebulizer. To do this, you can purchase a drug in the form of a special aqueous solution in a pharmacy.
In certain cases, combined expectorants are prescribed containing substances that have different mechanisms of action (Ascoril, Codelac Broncho, and others).
If necessary, for all types of cough, local antiseptics in the form of solutions, aerosols for treating the throat or lozenges may be additionally prescribed.
Folk remedies
Treatment of cough in children with folk remedies often gives positive results. Nevertheless, it is not worth using them as an independent therapy, especially with prolonged coughing.
After consulting a pediatrician, you can apply the following recipes:
- Black radish and honey. A root with a small piece of pulp is cut off from the root crop, the core is removed. The result should be a kind of "saucepan" with a lid. Inside, pour honey and insist for about a day. Next, take the medicine 5 ml three times a day. With this tool, you can treat a dry cough in a child.
- Honey compresses. A thin layer of honey is applied to the chest and back of the baby (avoiding the spine), covered with cling film, and put on a flannel shirt. It is best to leave such a compress overnight. The tool is most often used for coughing with sputum.
- Lime tea. A small handful of dried linden flowers is poured into a glass of hot water and left for 15 minutes. Tea is drunk regardless of food, a third of a glass three times a day.
- Pine kidneys and milk. 30 g of kidneys are poured into 0.5 l of hot milk and kept for 60 minutes. Further, the drug is taken orally at 50 ml 5-6 times a day. The medicine is used for all types of cough.
- Milk and mineral water. Warm milk is combined with non-carbonated mineral water in equal volumes. Drink half a glass 3 times a day. The remedy is especially good for wet coughs, as it helps release the bronchi from sputum.
In addition, traditional medicine recommends such means as badger fat, white cabbage juice and decoctions of various medicinal plants (coltsfoot, thyme, anise, etc.) for the treatment of baby cough.
Possible complications
A protracted cough of any nature can cause the following unpleasant phenomena:
- vomiting
- fainting;
- insomnia;
- involuntary bowel movements and urination;
- hemorrhages in the sclera of the eye;
- in severe cases, pneumothorax (accumulation of gas in the pleural cavity).
A cough of an infectious origin without medical intervention can become chronic, cause serious pathologies (pneumonia, etc.), give heart complications, and in very severe cases lead to the development of respiratory failure.
Preventive measures
One of the main measures to prevent coughing can be considered the prevention of acute respiratory viral infections and bacterial infections of the respiratory tract.
To do this, observe the following recommendations:
- avoid overcooling;
- Do not visit crowded places during the SARS epidemic and the common cold;
- periodically take vitamins;
- provide adequate physical activity;
- to be in the fresh air daily;
- provide good nutrition.
As a prophylaxis of dry barking cough in allergic children, it is recommended to ventilate the child’s room daily and conduct wet cleaning, limit or exclude interaction with pets. During the flowering period of allergen plants, antihistamines prescribed by a doctor should be given to the child.