Options for helping children with painful and uncomfortable sensations inside the ear can be different. If the child has a sore ear and fever, then pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs based on paracetamol are used to relieve symptoms. The use of ear drops is recommended to be discussed with a pediatrician.
Material Content:
The child’s ear hurts: the main reasons
Young children are often exposed to an infection that enters the nasopharynx and middle ear cavity behind the eardrum. The Eustachian tube connecting these departments is shorter in babies and is located almost horizontally (in adults - at an angle).
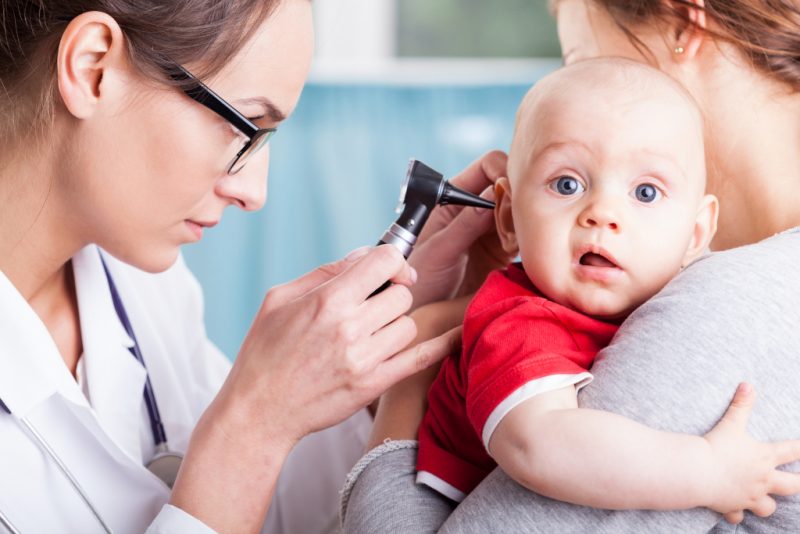

The main causes of pain in the ear in a child:
- inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous gland;
- injury during improper cleaning of earwax;
- diseases of the teeth located close to the ear;
- irritation with water that has fallen during bathing;
- complication after acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis, sinusitis;
- foreign body entering the ear canal;
- an allergic reaction to an insect bite;
- external or average otitis media (inflammation);
- eardrum rupture;
- chemical burn.
A foreign object in the ear canal causes pain in the ear during talking, chewing, and moving your head. A foreign body, if it is visible, parents can remove on their own with plastic tweezers with rounded ends. But it is best to ask for help in the treatment room of the clinic.
Colds, SARS - the most likely causes of acute otitis media in children under 5 years of age. Viral disease usually occurs without purulent discharge from the ear.
Initially, the respiratory syncytial virus, adenoviruses, rhinoviruses enter the nasopharynx. Pathogens then penetrate the Eustachian tube. Typical bacterial pathogens of bilateral purulent otitis media in children are pneumococcus, hemophilus bacillus, Staphylococcus aureus, moraxella. In the middle ear cavity, inflammation begins, and mucus accumulates. Pus appears, “melting” the eardrum and flowing out of the ear opening.
First aid: how to relieve pain
Inflammation of the ear is accompanied by otalgia. A child who knows how to talk, reports that "the ear hurts." Babies usually become more crying, sleep poorly, stretch their hand to the head.

With external otitis media, the pain is felt stronger in case of pressure on the cartilage located at the outer edge of the ear canal. Itching appears, fluid secretions accumulate. First aid for a child - rubbing the skin of the auricle and auditory canal with hydrogen peroxide, antiseptic preparations Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, tincture of calendula. Before use, add 1 part of boiled water.
Read also: hydrogen peroxide: indications for use
A compress is given to the child, but only until the boil “ripens” on the auricle or in the ear canal. You can mix vodka with warm water (1: 1), moisten gauze in a solution, squeeze and lay around the sore spot for 2 hours. Pre-lubricated skin with baby cream. The compress does not cover the auricle itself.
It is interesting:treatment of otitis media
Diagnosis of the disease: when to see a doctor
Signs of otitis media in a child can be recognized by complaints of congestion, noise and pain in the ears, and fever. The pain subsides after the opening of the hole in the eardrum. Mucus or pus begins to leak from the ear canal. Often there is a decrease in hearing (hearing loss).
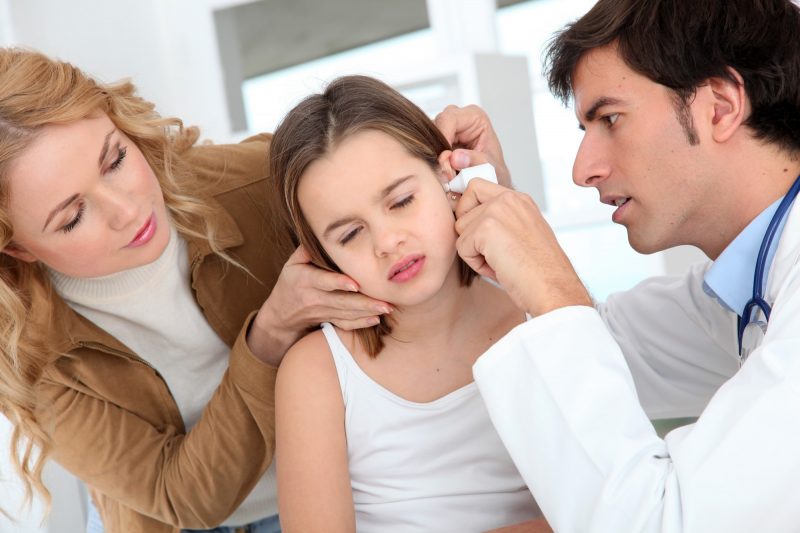

If the child has an ear inside, other characteristic symptoms of otitis media appear, then you should consult a pediatrician or pediatric ENT doctor.
Specialists use the otoscope to study the condition of the eardrum. With otitis media, this membrane changes color, becomes convex. If the disease is started, then a hole is formed in the eardrum through which bloody or purulent contents pour out.
In the clinic, the affected ear is washed with an antiseptic solution, a boil or abscess is opened with external otitis media. Or make a hole in the eardrum to remove accumulated fluid with otitis media (if necessary). Pus that does not flow from the cavity of the middle ear to the outside through the ear canal can penetrate the meninges, the brain.
Pain with and without temperature
Pain with otitis media is not always acute, most often it is aching. Normal temperature is maintained or rises to 37 - 38 ° С. When the ear hurts without fever, antipyretics and antibiotics are not prescribed. The purulent process in the ear can be recognized by the deterioration in the well-being of the child.

If the ear hurts and the temperature rises to 39 ° C, then they give a drug based on ibuprofen and paracetamol, which has an antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- For the treatment of infants, it is more convenient to use Cefecon-D rectal suppositories.
- Older children can take syrups or tablets Nurofen, Panadol, Naproxen.
- A child who has a severely sore ear is additionally prescribed antihistamines Fenistil, Zirtek, Zodak. They enhance the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect of ibuprofen, paracetamol and similar drugs.
The child’s ear hurts: what to do
If pain in the ear has arisen against a background of acute respiratory viral infection or sore throat, then mucus should be cleaned from the nasal passages. Blocking the Eustachian tube leads to difficulty in the outflow of fluid from the tympanic cavity and increased inflammation. For washing the nose, seawater preparations (Aqualor) and saline are used.Nasal drops of vasoconstrictor action are also used, but not more than 5-7 days.
Drug treatment
The use of pharmacy and folk remedies to eliminate pain in the ear in a child is recommended to be discussed with a pediatrician or pediatric otolaryngologist.
How to relieve pain with ear drops:
| Drug name | Act |
|---|---|
| Otipax, Otirelax | It is used for external and average otitis media as a local anesthetic and anti-inflammatory agent. For children from birth. |
| Otofa | An antibacterial drug for the treatment of otitis media, including perforation of the eardrum. |
| Sofradex | Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic drug. Contraindicated in the absence of integrity of the eardrum. Not applicable up to 12 months old. |
Ear drops immediately before use are heated to body temperature in a cup of warm water or in the hand. The child is laid on its side, instilled a solution, forced to lie down for another 2 - 3 minutes.
- Purulent otitis media in children is treated with amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (Augumentin, Flemoklav Solutab).
- For allergies to penicillins, azithromycin or cephalosporins (cefuroxime or ceftriaxone) are prescribed.
- Drops of Tsipromed or Nomax are instilled into the sore ear (in the absence of an opening in the eardrum).
- The nasal cavity is washed with saline, injected vasoconstrictor drops.
After taking antibiotics, the child recovers during the first two days. Within a few days of proper treatment, the earache subsides. Fully bacterial otitis media disappears in 10 days.
Alternative methods of treatment
A solution of boric alcohol is instilled in the ear 2 times a day, 1 drop to reduce pain and inflammation. A child older than 1 year old can be introduced into the external auditory canal with bandages from a bandage moistened with boron alcohol and left overnight. Either a cotton ball or gauze flagellum is moistened with camphor oil, injected into the ear canal.
If the child has an ear ache, the following actions can be performed to relieve pain with purulent otitis media:
- A tissue bag filled with warm salt is applied.
- You can use chamomile flowers or corn flour in the oven for a dry compress.
- As a softening agent, warm olive oil is instilled - 2 drops into the ear canal.
- Onion juice in the amount of 2 drops is injected into the ear canal for disinfection.
- Buried in a sore ear 1 drop of sea buckthorn oil with honey.
- They give a drink to a child over 2 years old tea with thyme grass or lemon and honey. Or 5 - 10 drops of propolis tincture 10% diluted in 1000 ml of water.
A compress with camphor oil for pain in the ear can be done if the child is older than 2 years.
- Camphor oil is heated in a cup of hot water.
- Wet with a bandage or a napkin made of cotton cloth, placed around the ear.
- Cover with wax paper and cotton wool on top, fix with a bandage.
What can not be done with pain in the ear in a child

- A contraindication for the use of any folk remedy and pharmaceutical drug is increased individual sensitivity to its components.
- A warming compress is not done when opening a boil, suppuration.
- Thermal procedures should be stopped when the temperature rises.
- Drops are not used without the advice of a doctor in a purulent process and perforation of the eardrum.
- It is forbidden to use alcohol solutions of high concentration for instillation into the ears.
Observance of all precautions reduces the risk of complications of otitis media. Prevention of ear pain in children consists in strengthening immunity, timely treatment of acute respiratory viral infections and allergies, removing water from the ear canal immediately after bathing.