The ear is a rather complex organ in structure and function. Not the last role in its functionality is played by the eardrum. Injury to this septum can cause discomfort in the ear and even become a health hazard.
Material Content:
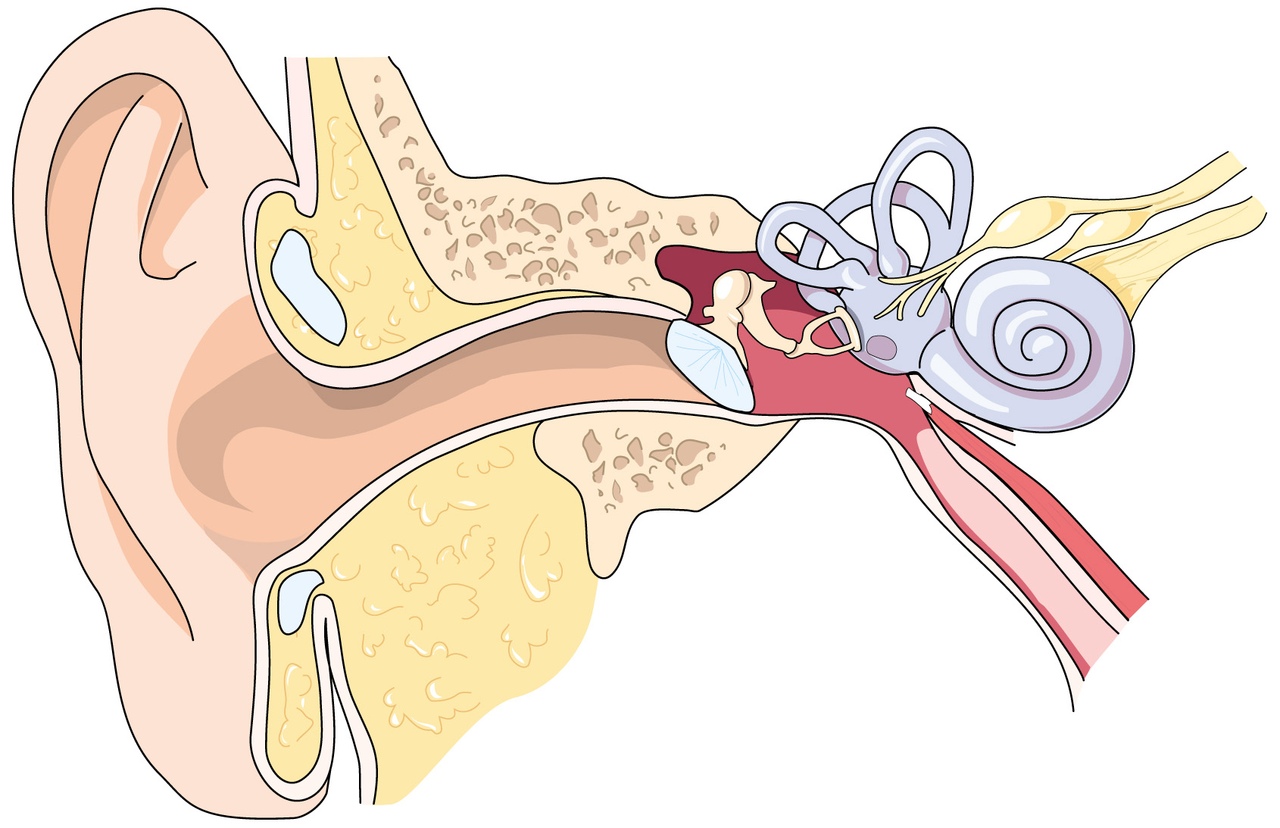
The structure of the eardrum
The structure of the membrane is complex. The membrane has three layers:
- Outer. Represented by an accumulation of epithelial cells. Damaged, this layer can recover itself.
- Average. Its again - elastic fibrous tissue. The latter is sensitive and quite tight. Fibrous tissue fibers are located in two directions and form a kind of mesh. After the break, they can no longer grow together. It is behind this layer that the so-called tympanic nerve, which is part of the middle ear, is located.
- Interior. In fact, this is a kind of mucous lining that protects the membrane from drying out. The smallest muscles regulate tension, and the cells of this layer are able to recover very quickly. When exposed to excessively loud, harsh sounds, the tension weakens and the sensitivity of the hearing organ decreases.
Note. The eardrum has a diameter of about 1 cm. This septum is located in the area of the temporal bone, located at a certain slope.
What are the functions of the membrane?
The eardrum helps the acoustic wave reach the organs of hearing. Caught by the shell of the ear, these waves gradually penetrate inside.Succumbing to the sound effect, the membrane vibrates, but the human brain can only perceive mild impulses that still need to be "reformatted" into sound. This process is carried out in the inner ear.
Many people wonder where the partition transfers vibrations and why it does not push through under the influence of atmospheric pressure. Directly behind the membrane are the anvil, malleus and stapes - the smallest bones of the human body. It is this trio that accepts all vibrations made by the membrane. The amplified vibrations go further, while the fluid filling the inner ear begins to flutter reflexively.
What could cause injury
The main injury of the eardrum is the gap. And although the thickness of the membrane is very small (approximately 0.1 mm), it is considered superelastic. It is for this reason that only extremely strong, harsh sound or internal or external pressure can damage or tear it.
The following factors can lead to membrane injury:
- nearby shots and explosions;
- excessively rapid deep diving;
- head injuries, damage to the temporal part;
- sulfuric cork;
- mechanical damage;
- getting into the ear of a foreign body.
Purulent otitis media can also violate the integrity of the septum. Accumulated pus presses on the membrane, deforming it.
Mechanical damage to the inner ear
Even a banal strong kiss in the ear, creating a vacuum, can cause a rupture of the membrane. In addition, the membrane is often damaged when cleaning with inappropriate items. Some people may note that their eardrum burst even when sneezing with their nose stuffy at the same time.
The resulting small tear of the ear membrane, called the perforation of the tympanic membrane, reduces the elasticity of the membrane. Although it can recover gradually, sound perception can be reduced.
A complete rupture of the membrane leads to deafness, since it is impossible to hear without this layer.
Symptoms of Damage
The following main symptoms of perforation of the eardrum are distinguished:
- sharp pain;
- fluid discharge or ear bleeding;
- sudden hearing loss;
- noise, ringing in the ears;
- stuffy ear.
The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage to the membrane. When they are insignificant and affect only the outer layer, a noticeable decrease in hearing is not observed.
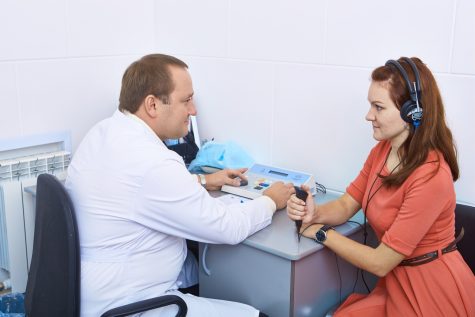
Diagnostic measures
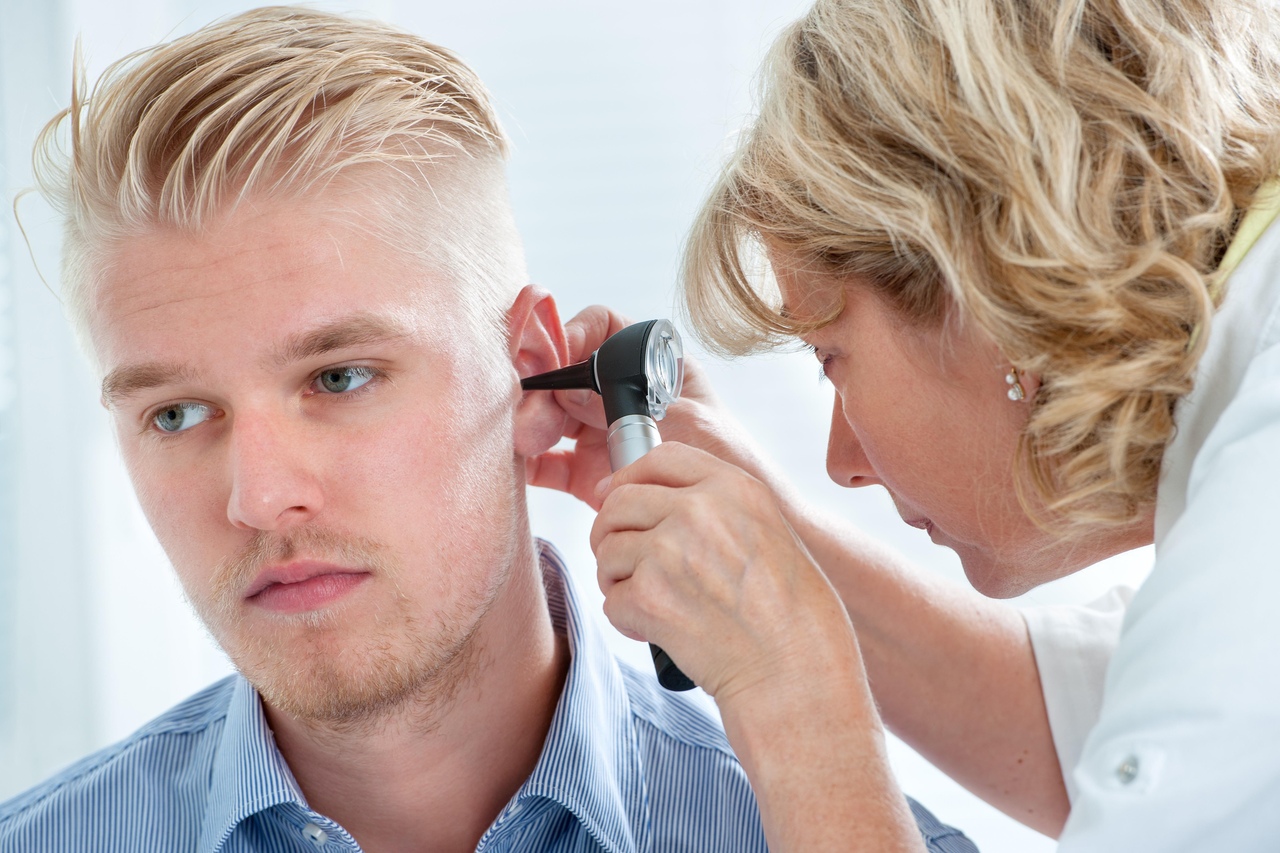
The basic method for diagnosing the condition of the eardrum is otoscopy. It is carried out by placing a special funnel in the patient’s ear canal. In this case, the ear shell moves back and up. In addition, the doctor makes a fence secreted from the ear to monitor for possible infections in the ear.
Additional methods for diagnosing the condition of the eardrum include:
- audiometry;
- vestibulometry;
- stabilization;
- electrocochleography;
- tuning fork research.
Directly before the diagnostic procedures, the doctor collects the patient’s complaints, interviews him and examines him.
Eardrum Injury Treatment
Minor eardrum injuries often heal themselves. In this case, the patient should observe a gentle rest regimen and not expose the ear canals to any effect.
Note. If damage to the membrane was provoked by purulent otitis media, the patient may be prescribed pneumatic massage of the tympanic membrane. This vacuum effect is created by changing the low and high air pressure to the membrane, as a result of which its vibrations are stimulated, helping to get rid of purulent accumulations and reduce the symptoms of otitis media.
There are two main methods of treating tympanic membrane injuries: medication and surgical.
The drug method involves applying a paper patch to a small damaged area of the membrane.Such manipulation is performed exclusively by a specialist doctor. After a few days, the patch changes to a new, sterile one. Such procedures will need 3-4. This will speed up healing and prevent infection. If residual dirt or blood clots accumulate in the wound, the doctor with extreme care cleans them with a cotton swab, and then treats the cavity with alcohol. The latter procedure is necessary to eliminate the possible development of inflammation. Alcohol processing ends with the location in the ear of a twisted cotton swab.
Additionally, in order to avoid infection, a specialist can recommend antibiotic-based drops (Otof, Tsipromed, etc.). Their task is to eliminate the unfavorable microflora.
The surgical method is used if drug therapy did not bring the expected results or the gap was extremely wide. The restoration of the eardrum is called myringoplasty. They perform it under general anesthesia. The doctor makes a large incision behind the patient’s ear. From this place, a piece of tissue is taken. It is with this patch that the damaged membrane will subsequently be closed. The taken piece is sewn to the damaged membrane with self-absorbable threads. They themselves will be eliminated a couple of weeks after the wound has completely healed. After the intervention, an antibiotic-soaked swab is placed in the patient’s ear to avoid infection.
How to prevent injuries
To prevent various injuries of the eardrum, a number of recommendations should be followed:
- Seek medical attention immediately if hearing impairment occurs.
- Carefully and thoroughly hold the toilet of the ears.
- Observe the children, not allowing them to place foreign objects in the ear.
Tip. Sometimes the eardrum is damaged during air travel. This phenomenon can be prevented in the following ways:
- fill the ear canal with ear plugs;
- use sucking candy;
- massage the ears with the index finger;
- open your mouth when taking off and landing the aircraft.
Gunners and people working with technological explosions are also advised to open their mouths immediately at the time of the explosion. This will "smooth out" the pressure difference applied to the membrane from two sides.
The eardrum is an intra-ear membrane, characterized by a complex structure. Despite its elasticity, in some cases trauma to this layer can occur, leading to numerous problems, up to deafness. To avoid such situations, precautionary measures to protect your hearing from foreign objects and excessively sharp and loud sounds will help.