Among the many varieties of chronic human diseases, autoimmune hepatitis is particularly prominent. This pathology of the liver can provoke multiple health problems and even lead to irreversible consequences. Is this disease amenable to therapy, and can it be avoided?
Material Content:
What is autoimmune hepatitis
An autoimmune liver disease accompanied by a chronic inflammatory process is called autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). At the same time, autoimmune antibodies are clearly monitored in the blood serum. In other words, the human immune system attacks liver cells (hepatocytes), which over time are completely destroyed, and the work of the organ can stop altogether.
This pathology was first mentioned in the 30s of the last century. And already in 1950, a Swedish doctor named Waldenstrom monitored chronic hepatitis with jaundice in 6 young women. During these years, the disease was also called lupoid hepatitis due to the similarity of symptoms with manifestations of lupus erythematosus.
Some statistics. AIH is often diagnosed in women under 30 years old and after 50 years. This disease progresses rather quickly, and therefore it is extremely important to start timely therapy.
Causes of the virus
The causes of hepatitis are still poorly understood and unclear. It is believed that the basis of this disease is exclusively genetic. Nevertheless, the child of parents suffering from this ailment does not always notice the manifestations of AIH.
Additional alleged reasons for the development of AIH are:
- transferred hepatitis A, B and C;
- infections provoked by the causative agents of measles, herpes, Epstein-Barr;
- the effect of a number of drugs.
Modern research aims to identify factors that trigger the disease.
Forms of the disease
Doctors divide autoimmune hepatitis into 2 types:
- It is characterized by the presence in the blood of autoantibodies ANA and SMA. About 80% of all patients are affected by this particular form of hepatitis A, and 70% of them are women. In the absence of timely treatment, it can transform into cirrhosis of the liver. This kind of disease is especially common in Western Europe and the United States.
- It is characterized by tracking in the blood of autoantibodies anti-LKM-1 and / or anti-LC1, anti-LC3. 95% of all cases are children. The biochemical activity of this form of the disease is higher, a complication in the form of cirrhosis occurs much more often.
Note. Some doctors tend to recognize the presence of 3 types of AIH. However, its existence is in doubt. Traditional medicine calls for considering this variety not as an independent form, but only as a special case of type 1 hepatitis.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Typical symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis include:
- enlargement of the liver in size;
- digestive system failure: vomiting, nausea, etc .;
- dermatological pathologies;
- a feeling of heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium;
- “Butterfly symptom” (redness of the skin on both sides of the nose);
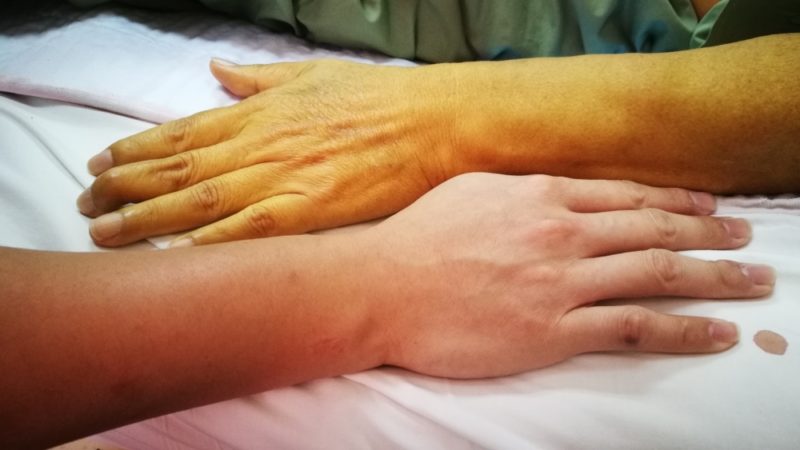
- jaundice;
- malfunctions of the menstrual cycle.
AIH is almost always accompanied by gastritis, in some cases - an increase in the spleen. The acute phase of the disease is characterized by the presence of abdominal dropsy. Additionally, the functionality of the heart, thyroid gland, intestines, etc. may be impaired.
Diagnosis and treatment of the virus
Diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis is not an easy task, since it must be differentiated with many similar diseases. A diagnosis can only be made using various studies.
When accepting the patient, the doctor carefully listens to his complaints, examines the skin of the patient, measures the temperature, probes the stomach.
Additionally, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- blood and stool tests (help evaluate the features of the liver);
- liver biopsy;
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs (allows you to track the condition of internal organs);
- CTG of the liver (helps to see the state of organs in more detail);
- elastography (is to identify the proliferation of scar tissue).
AIH should be differentiated with the following diseases: Wilson’s disease, chronic viral, alcoholic and drug hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatic dystrophy.
AIH is treated through pathogenetic therapy, designed to restore body functions and normalize metabolism.
Today, one or more of the following methods for eliminating hepatitis symptoms are relevant:
- Diet therapy. The patient should exclude fried, spicy, fatty dishes from the menu, switching to fractional nutrition, including more fruits, vegetables, fish, etc. in the diet.
- Drug treatment. It involves the use of the following types of drugs: glucocorticoids (inhibit the formation of antibodies), immunosuppressants (reduce the activity of immunity), medicines of ursodeoxycholic acid (protect hepatocytes).
- Surgical intervention. Recommended for patients who could not restore liver functionality by other methods. Typically, such operations involve transplantation of liver tissue from a donor, which is often the patient’s relative.
The choice of treatment method depends on the condition of the patient’s liver, as well as the presence or absence of complications.
Autoimmune Hepatitis Disability
All patients with the first type of chronic hepatitis are considered able-bodied.The second type of disease also provides for the preservation of working activity under the condition of slow progression or short exacerbations.
During the active phase of AIH, a temporary disability and the development of complications occur. On average, a sick stay in this case can last from 15 to 60 days.
Patients with chronic hepatitis may be assigned disability:
- III group. Subject to the limited ability of self-care patients at stage 2 AIH and lasting from 4 to 6 weeks exacerbations.
- II group. Subject to the limited ability to self-care and prolonged exacerbations up to 6-8 weeks, as well as moderate or severe degree of impaired liver function.
- I group. Subject to the loss of mobility and self-care, as well as the rapidly progressing course of the disease.
To obtain the first group of disabilities, the patient must also be diagnosed with liver failure, pancreatic dysfunction and damage to other organs.
Preventative measures
Autoimmune hepatitis involves exclusively secondary prevention.
The latter includes:
- systematic observation by a gastroenterologist;
- lack of excessive physical and emotional overload;
- dieting;
- monitoring the activity of liver enzymes, autoimmune antibodies.
Autoimmune hepatitis in the absence of timely treatment can completely disrupt the functionality of the liver. The good news is that modern medicine can eliminate the symptoms of the disease at an early stage, which means that the prognosis in this case is favorable. Prevention measures taken will help reduce the risk of AIH.