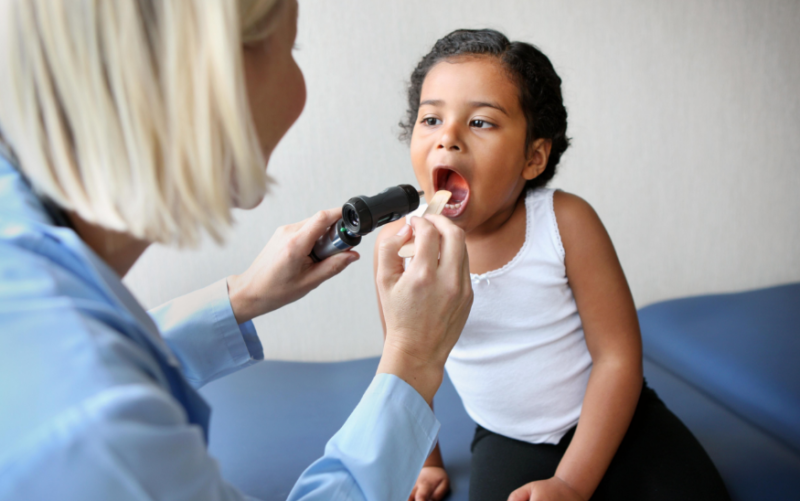
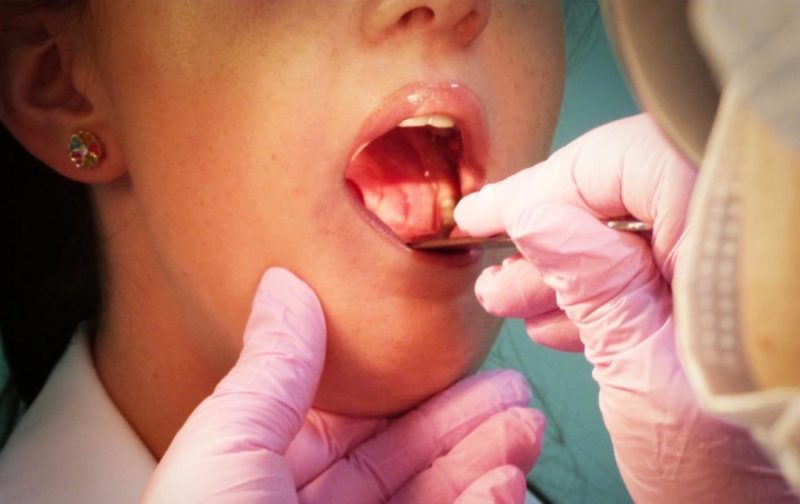
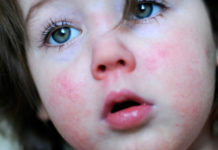
Palatine tonsils are a “target” for pathogens and a barrier to infection. Antibiotics for angina in children are indicated for bacterial etiology of inflammation and for the prevention of purulent complications. For babies, this group of drugs is prescribed even with viral tonsillitis to prevent superinfection.
Material Content:
What is angina in children, how does it manifest
Palatine tonsils (lat. Tonsillae) - a paired organ, an accumulation of lymphoid tissue cells between the oral cavity and pharynx. In everyday life, they received the name "glands." Tonsils serve as a barrier to infection from the external environment, neutralize pathogens before entering the body through the pharynx, larynx and lower sections of the respiratory system.
Infants rarely have tonsillitis, since at this age the tonsils are underdeveloped. Intensive growth of lymphoid tissue occurs in 1 to 3 years. The immune system is only being formed, pathogens more easily penetrate the glands, cause an infectious disease.
Inflammation of the tonsils in babies is usually of viral origin.
Bacterial tonsillitis is often diagnosed in preschoolers and schoolchildren who turned to pediatricians with a sore throat. Inflammation develops in the tissues of the throat, swelling and redness accompany this process. The size of the tonsils increases, the clearance above the root of the tongue decreases, the oropharynx narrows and swallowing is difficult.
A mixed infection may be the cause of acute tonsillitis in the colds season. Children are more likely to tolerate symptoms of inflammation, especially sore throat, fever.
When antibiotic therapy is indicated for a child
With a catarrhal form of angina, the sore throat is moderate, the temperature is slightly elevated. Recovery occurs in 5 to 7 days. Antibiotics are not recommended for use with mild manifestations of the disease, they will not help with a viral infection. However, in children more often and faster than in adults, a purulent complication of tonsillitis develops.
If left untreated, the mild catarrhal form can go into follicular and lacunar. Pus is formed, which is due to the activity of pathogenic strains of bacteria from the genus Streptococcus.
Treatment of angina with antibiotics is carried out with symptoms of a purulent process. These include a yellowish or white coating, pus vesicles on the surface of the glands, general intoxication (fever, vomiting).
There is a recommendation for pediatricians to prescribe antibiotics for purulent tonsillitis based on the results of the tests. Previously, a microbiological examination of the throat smear is carried out in the laboratory. With a low probability of developing streptococcal infection, a small patient does not need this analysis.
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus can be determined using a rapid analysis of pharyngeal mucus. Test strips "Streptatest" are used. The time to get the result is 5-10 minutes, the sensitivity of the rapid diagnosis reaches 95%.
Categories of medicines used for angina
The catarrhal form of the disease often occurs without fever or with a slight increase in temperature. Other symptoms are also less pronounced. Mild forms of tonsillitis are treated with local drugs.
Antimicrobial effect is exerted by sprays and lozenges:
- "Bioparox";
- Miramistin;
- "Lizobakt";
- "Faringosept."
The strength of the manifestations of tonsillitis largely depends on the body's response to the infection, toxins, inflammatory mediators. With fever, paracetamol or ibuprofen is given. Trade names of children's preparations with these active components: Panadol, Kalpol, Tylenol, Tsefekon D, Nurofen, Advil, Maxikold. Aspirin, other drugs with acetylsalicylic acid are contraindicated in children.
Ibuprofen has a stronger and faster antipyretic, analgesic effect.
Antihistamines significantly improve the patient's condition (along with NSAIDs): eliminate throat irritation, reduce swelling of the tonsils. Drops, syrup or tablets with anti-allergic effect give 1 time at night.
Local remedies will not replace the treatment of tonsillitis in children with systemic drugs. Antibiotics act on the cause of bacterial tonsillitis, are prescribed for severe illness, purulent complication. Drugs appropriate to the type of pathogen are used.
List of effective drugs
In 2012, the Ministry of Health of Russia ordered doctors to indicate international nonproprietary names (INN) when prescribing medicines to patients. The drugs can be identical in composition, are complete analogues, although the trade names and prices differ. Domestic medicines are 5-10 times cheaper than foreign medicines.
Beta hemolytic streptococcus is sensitive to penicillins.
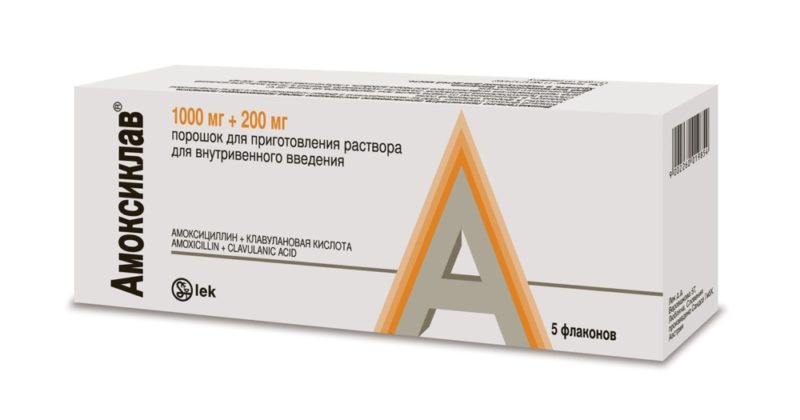
Amoxicillin from this group has high bioavailability, good tolerance. It is considered the "gold standard" for the treatment of streptococcal tonsillitis in children. In combination with clavulanic acid, amoxicillin is less prone to destruction by bacterial enzymes.
List of antibiotics:
- "Augmentin EU" (differs in the ratio of components).
- "Flemoklav solyutab."
- Amoxiclav.
- "Augmentin."
- "Ecoclave".
- "Arlet."
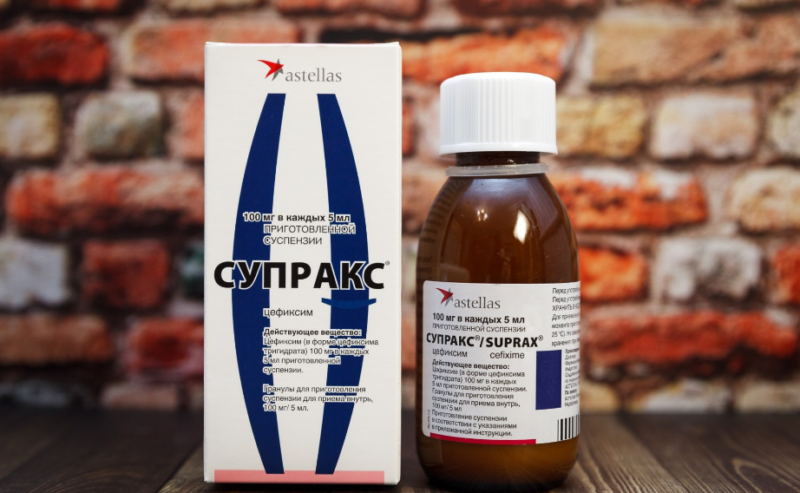
"Cefixim" from the group of cephalosporins is prescribed for hypersensitivity to penicillins. The trade name of the drug is Suprax. Cephalexin from the same group is used for severe illness.
Rarely, with tonsillitis in children, the macrolide antibiotic "3 days" is used - azithromycin (the shortest course of use).Trade names: "Sumamed", "Azitroks", "Hemomycin." Azithromycin quickly reaches a high concentration in plasma and retains it longer than other antibacterial agents.
Clinical trials of the antibiotic josamycin have been conducted. The trade name for the tablets is Wilprafen Solutab. The researchers obtained results proving the effectiveness of the drug in acute streptococcal tonsillitis and pharyngitis in children. Undesirable manifestations were observed in 4 - 9% of cases.
Features of the treatment of children of different ages
Pediatricians prescribe antibiotics, NSAIDs in the form of ready-made syrups or granules for the preparation of a suspension for patients under 8 years of age. Typically, a dosing device (cup, pipette) is attached to the package. The preferred dosage form for infants is candles.
Syrups and suspensions for babies up to 3 years old are diluted with a small volume of water before use. It is advisable to give the medicine with food to prevent a negative effect on the digestive tract.
High dosage tablets and capsules are not prescribed for young children. It is difficult to correctly calculate the active substance and divide the tablet in accordance with the age and weight of the child. Capsules are not recommended to break - the shell is needed to protect the contents from destruction in the stomach.
An antipyretic, anti-inflammatory drug from the category of non-steroidal (NSAIDs) is given to a temperature-sensitive child at T ° C above 38.1. If earlier the baby had cramps, then the drugs of this group should be taken already at 37.5 ° C.
For sore throat in infants older than 3-6 months, you can use dental products (Kalgel, Kamistad Baby, Holisal). The analgesic effect is manifested a few minutes after treatment of the oral cavity.
Rules for taking antibiotics
According to the doctor of the Children's Hospital. Filatova N. Beloborodova (Moscow), an antibacterial agent is most effective at the onset of the disease. Therefore, pediatricians are most often prescribed an antibiotic after an initial examination of a child without data from a microbiological analysis. The "starting" drug may not affect the infection. Then the inflammatory process does not stop, but intensifies, complications develop, hospitalization is required.
Amoxicillin with clavulanic acid is taken 2 times a day. The duration of antibiotic therapy is 5-10 days, in severe cases - 2 weeks.
The antibiotic inhibits the growth of pathogenic microflora, so the child feels better after 2 days.
Suprax is given for at least 7 to 10 days. Multiplicity of admission - 1 or 2 times a day. “Sumamed” or “Hemomycin” is prescribed for infants. Apply 1 time per day for 3 days.
Preventive actions
- During seasonal epidemics, it is not recommended to visit crowded places with a child where there is a chance of infection.
- You should regularly clean the house, apartment, ventilate the premises in the absence of children.
- The child's nutrition should be rational, and drinking should be plentiful, fortified.
- Herbal teas with chamomile, sage, lemon, rosehip, honey, carrot juice, blackcurrant have a preventive and therapeutic effect on the mucous membrane of the throat, tonsils.
- A child with a high temperature is shown bed rest. Compliance with this and other rules will help to avoid complications of tonsillitis.
After improvement, the patient can adhere to the usual daily routine with the exception of visits to child care facilities and outdoor games. If the body temperature returned to normal, swimming and walking in the fresh air are allowed.
Young children are more susceptible to infection of the ENT organs, more often receive antibiotics.
The immune system weakens, the risk of repeated infections increases. Antibacterial therapy in the first 5 years of life is dangerous for the development of allergic reactions, intestinal dysbiosis.
For the prevention of microbiome disorders, children of different ages are assigned probiotics from the following list: Acipol, Bactistatin, Bactisubtil, Bifidum-Multi, Bifiform Baby, Yogurt, Lactobacterin Linex, Maxilak Baby, Symbiolact. Thanks to the drugs of this group, the restoration of intestinal microflora after antibiotic therapy takes place within 4-6 weeks (instead of six months).
In addition, the normalization of the composition of the microbiome helps to strengthen immunity. The child is less likely to have ARVI, tonsillitis, and if infection cannot be avoided, then recovery comes faster.