The time of carrying a child in a person is quite long, and during this difficult period, the mother does not exclude the occurrence of various diseases. Some of them require antibiotic treatment. It is important to understand in what cases Amoxiclav can be prescribed during pregnancy, and when to postpone therapy.
Material Content:
- 1 Is it possible to take Amoxiclav in 1, 2, 3 trimesters
- 2 Forms of release and composition of the drug
- 3 In which cases a drug is prescribed
- 4 Instructions for use at different stages of pregnancy
- 5 The effect of Amoxiclav on the fetus
- 6 Drug interaction
- 7 Contraindications, side effects and overdose
- 8 How to replace an antibiotic
Is it possible to take Amoxiclav in 1, 2, 3 trimesters
In the early stages of pregnancy, antibiotic treatment is best avoided. The embryo is not yet protected by the placenta, therefore, it can suffer from the action of chemicals. But in case of acute need for antibacterial therapy, “Amoxiclav Quicktab” can be prescribed to the patient in the 1st trimester.
"Amoxiclav" in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy can be used without fear. This time is considered the safest for taking antibiotics. The formed placenta reliably protects the fetus from the effects of physical and chemical factors.
The third trimester of pregnancy is the most controversial in terms of antibiotic therapy. Amoxiclav can be used as an emergency prevention of intrauterine infection, but during this period, the side effects of the drug affect not only the mother, but also the child. These risks should be considered before starting treatment.
Forms of release and composition of the drug
The medicine is available in several forms. This helps to choose the method of application and calculate the optimal dosage.
- The minimum concentration of the active component in Amoxiclav tablets is 250 mg, which corresponds to the proportion of amoxicillin in it. The original tablet is white and has an octagonal shape convex on both sides. It is distinguished from others by impressions “250/125” and “AMC” from different sides. In a glass vial, 15, 21 or 20 pieces are embedded.
- There are also drugs with 500 mg and 875 mg of the active substance. At the same time, the first have a smooth shell, and the second - a print of "875/125" and "AMS" from different sides of the tablet. If you break it in half, in the middle will be a yellowish composition. The packaging of thin cardboard contains 2/3/4 cell forms of 5 tablets or 2 of 7 pieces.
- Amoxiclav also exists in the form of a yellowish or white powder, from which a suspension of the same color is made. This dosage form is mainly used for children. 5 ml of the finished medicine may contain 125 mg, 250 mg or 400 mg of amoxicillin and 31.25 mg, 62.5 mg and 57 mg of clavulanic acid, respectively. In the package with the first dosage of 25 g of the drug, which is enough for 100 ml of solution, and with the second and third, there are options for 8.75 g per 35 ml, 12.5 g per 50 ml, 17.5 g per 70 ml and 35 g 140 ml.
- In some cases, Amoxiclav injections are prescribed. To do this, use a solution that is prepared from a yellowish or white powder. It may contain 500 mg or 1000 mg of amoxicillin in 1 bottle and 100 mg and 200 mg of clavulanic acid, respectively. In one package of thin cardboard 5 such bottles.
Important! The effect of Amoxiclav is provided by two components: amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Their interaction enhances the bactericidal effect of each several times.
Pregnant women are most often prescribed Amoxiclav Quicktab. These are soluble tablets, in 1 piece of which contains 500 mg or 875 mg of amoxicillin and 125 mg of clavulanic acid. They have an octagonal shape, the smell of fruit and a pale yellow color. In one cell package there are 2 pieces, and in a pack of thin cardboard there are 5 or 7 such blisters.
In which cases a drug is prescribed
The antibiotic Amoxiclav is characterized by a wide range of effects on bacteria.
Therefore, he found application in the treatment of a whole list of diseases:
- gonococcal infection;
- acute and chronic sinusitis;
- chancroid;
- unspecified infection caused by bacteria;
- pharyngitis of acute and chronic course;
- peritonitis;
- tonsillitis of bacterial origin;
- acute or chronic bronchitis;
- inflammation of the middle ear of an unspecified etiology;
- duodenal ulcer or stomach;
- tonsillitis of a chronic course;
- liver abscess
- acute inflammation of the middle ear of a purulent nature;
- pneumonia of unspecified genesis;
- pancreatic necrosis;
- parapharyngeal and retropharyngeal abscess;
- gallbladder inflammation;
- unspecified periodontal pathology;
- cholangitis;
- intestinal diverticulum;
- unspecified inflammatory disease of the female reproductive system;
- osteomyelitis;
- trauma to internal organs;
- unspecified pathology of the duodenum and stomach;
- contact with a poisonous animal;
- undetermined urinary tract infection;
- gonococcus disease of the female reproductive system;
- systemic pathology of connective tissue of unspecified origin;
- inflammation of the appendix of unclear etiology;
- performed or upcoming surgical treatment;
- unspecified localized infection of fatty tissue or skin;
- bone pathology of unclear etiology;
- attack of a non-toxic arthropod or insect;
- chlamydia
- leptospirosis;
- pyelonephritis;
- urethritis, cystitis;
- premature rupture of membranes;
- odontogenic infections.
When diagnosing one of the diseases, Amoxiclav becomes the drug of choice. For pregnant women, this medicine is preferred, as it is approved for use in all trimesters.Before prescribing, it is important to test for sensitivity to amoxicillin in the bacteria that caused the disease. This will ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
Instructions for use at different stages of pregnancy
The dosage of the drug is selected for the person, depending on his condition, gender, age and weight. In pregnant women, the appointment may be due to the gestation period.
Attention! The duration of therapy is limited to 14 days, but is at least 5 days.
The medicine is better absorbed when taken before meals. So it has less damage to the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Adult women are prescribed 1 tablet with 250 mg of the active substance 4 times a day. Antibiotics are best taken at regular intervals - every 8 hours. In case of severe disease, the dosage of the active substance is increased to 500 mg.
In the later stages of pregnancy, kidney problems often occur.
In the instructions for use for this case, specific dosages of the drug are indicated:
- in the absence of urine, the time between tablets increases to 48 hours;
- if creatinine clearance is from 10 to 30 ml / min, patients are prescribed 250 mg tablets for mild and 500 mg for severe 2 times a day;
- with creatinine clearance less than 10 ml / min, a 500 mg or 250 mg regimen is used once a day, depending on the severity of the condition.
If the patient's condition requires an immediate antibacterial effect, the drug is administered intravenously. To do this, take 1.2 g of powder and administered every 8 hours for mild and every 6 hours for severe. For preventive purposes, injections are given up to 4 times a day.
If kidney function is impaired, the dosage is selected according to the patient's condition:
- with creatinine clearance from 10 to 30 ml / min, the first injection of the drug is 1.2 g, and the next 600 mg after 12 hours;
- if the indicators are up to 10 ml / min, the interval of subsequent injections is increased to 24 hours;
- in the absence of urine, the time increases to 48 hours
When the patient's condition improves, she is transferred to the oral form of the pharmaceutical product.
In late pregnancy with premature rupture of the membranes, intravenous infusions may be prescribed. This helps to prevent bacteria from entering the fetus.
The effect of Amoxiclav on the fetus
Prevention of intrauterine infection in the fetus with Amoxiclav in case of premature rupture of the bladder may increase the risk of necrotizing colitis in the child. Such children require observation after birth by a pediatrician and gastroenterologist. No other effect of the antibiotic on the fetus was found.
Drug interaction
"Amoxiclav" is referred to as potent drugs.
Therefore, it interacts with a large number of drugs:
- glucosamine, aminoglycosides, antacids, laxatives - impair absorption;
- Vitamin C - increases absorption;
- tubular secretion blockers, NSAIDs, allopurinol, diuretics, phenylbutazone - increase the amount of amoxicillin in the blood;
- methotrexate - enhances toxic activity;
- allopurinol - increases the risk of exanthema;
- ethinyl estradiol - increases the chances of breakthrough bleeding;
- rifampicin, tetracyclines, macrolides, sulfonamides - weaken the effect of each other;
- indirect anticoagulants - act stronger than usual;
- probenecid - delays amoxicillin in the body;
- aminoglycosides - complete incompatibility;
- mycophenolate mofetil - the concentration of the drug in the blood plasma decreases.
Do not allow the mixing of Amoxiclav in a liquid state with other drugs. Also, do not add dextran, dextrose and sodium bicarbonate to it. Means for prescribing should be free of proteins, traces of blood and fat. Otherwise, the activity of amoxicillin decreases.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
Amoxiclav is considered a powerful antibiotic.
Therefore, it is not surprising that there are contraindications for its appointment:
- an allergic reaction to substances in the composition of the drug;
- hypersensitivity to cephalosporins, penicillins and other beta-lactams;
- lymphocytic leukemia;
- liver pathology caused by drug components in past applications;
- mononucleosis of an infectious origin;
- phenylketonuria.
With non-compliance with the dosage and ignoring contraindications to the use of the drug, side effects occur.
The medicine negatively acts in several directions:
- Gastrointestinal tract: dyspeptic symptoms, impaired appetite, pain in the abdomen, inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract, impaired liver function;
- blood: lack or excess of blood cells, worsening of coagulation;
- immune response: rash, itching, redness, vascular inflammation, anaphylactic reactions, dermatitis, epidermal necrolysis;
- superinfection (candidiasis);
- excretory system: the appearance in the urine of blood and crystals, inflammation of the interstitium of the kidneys;
- CNS: convulsive syndrome, headaches, increased anxiety, dizziness, irritability.
If you accidentally take too much medicine, an overdose may occur. Its symptoms are limited to dyspeptic disorders, pain in the abdomen, irritability, sleep disturbance, dizziness. Convulsive syndrome develops less often. If these signs are detected, you should consult a doctor for medical help.
How to replace an antibiotic
Self-replacement of drugs is unacceptable. But in some cases, the doctor may choose safer analogues for the treatment of pregnant women.
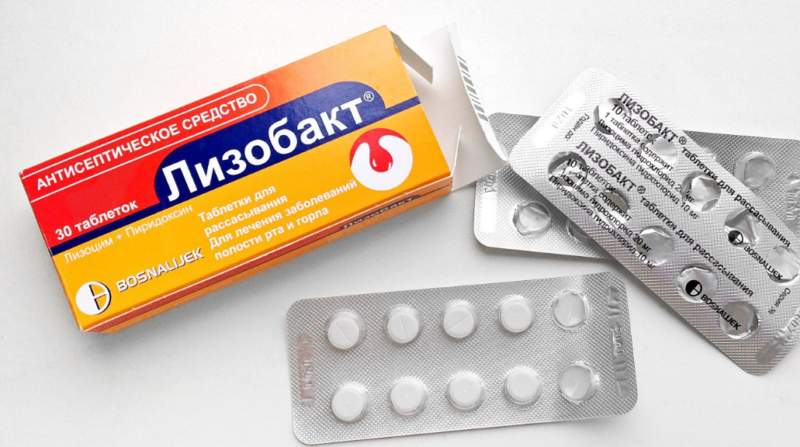
- In the treatment of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract at an early stage, "Lizobact" is often prescribed. This tool is approved for use in children from birth and is suitable for lactating and carrying women.
- With bronchitis, licorice root or Althea officinalis extract is effective. But they can not be used by pregnant women in the form of syrup due to the alcohol in the composition. Therefore, drugs are selected only in tablet form.
An antibiotic during pregnancy is prescribed only in extreme cases. Refusal from it causes a threat to the life and health of both the mother and the fetus. Among drugs with antibacterial activity, Amoxiclav is one of the safest, and is recommended for women carrying a child.