Inflammatory processes on the oral mucosa in children and adults are a common phenomenon, but potentially dangerous. Especially aphthous stomatitis, the development of which, according to dentists, may indicate impaired functionality of internal organs. Timely contacting a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease is the best way to avoid its transition to a chronic form.
Material Content:
What is aphthous stomatitis
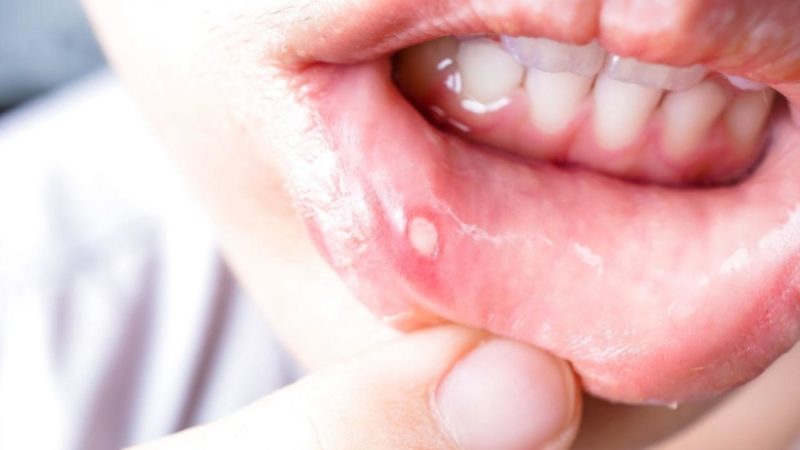
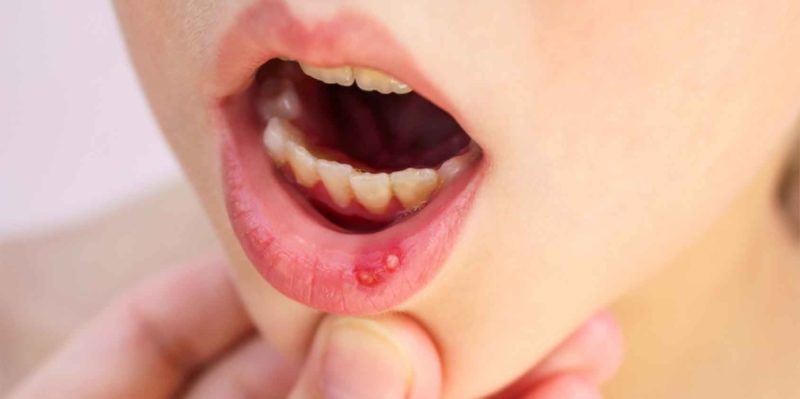
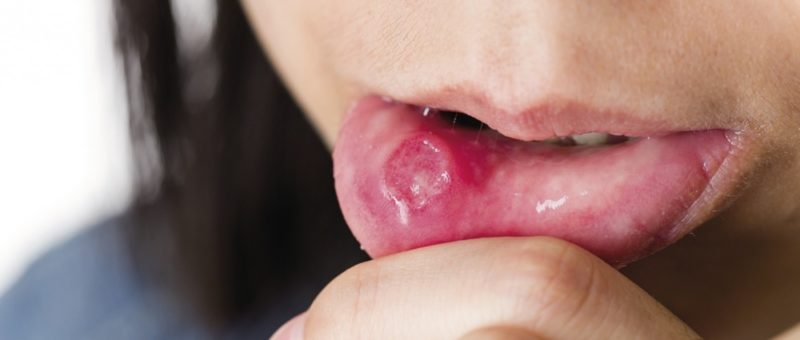
Aphthous stomatitis is a pathological condition of the oral mucosa, in which the appearance of aphthae is observed. In dentistry, the term “afta” implies ulceration of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity in the form of erosive and ulcerative formations.
Such mucosal lesions are accompanied by soreness and significantly impede the ability of speech, as well as chewing food.
With a therapeutic effect, aphthae in the mouth quickly heal and disappear without a trace within a week. In the absence of drug therapy, the disease is prone to relapse.
In this case, the symptoms of aphthous stomatitis periodically return. In the presence of concomitant diseases or a weakening of immunity, the disease takes the form of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis.
Like other types of stomatitis, aphthous lesion is not considered contagious, provided that the development of the disease was not a result of human infection.
Causes of adults and children
The mechanism of development of aphthous stomatitis, as well as its etiological prerequisites, is not yet completely clear to doctors. It was established that the disease is actively developing against the background of a decrease in immunity and under the influence of various factors:
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- irritating or traumatic effects on the mucosa - too hot or hard foods, drinks, dentures, toothpaste with sodium lauryl sulfate;
- pathological processes in the stomach and intestines;
- helminthic invasion;
- hypovitaminosis;
- deficiency of iron, folic acid, zinc, selenium;
- dysfunctions of the nervous system;
- chronic infections of the nasopharynx;
- genetic predisposition.
Often the formation of erosion on the oral mucosa leads to the absorption of a large number of tomatoes, pineapples, citrus fruits, chocolate, seafood or spices.
In women, exacerbation of aphthous stomatitis can be observed during menstruation and with a change in hormonal levels.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Aphthous stomatitis in children and adults develops differently.
In children, the disease most often occurs after four years. Its beginning is signaled by a change in the behavior of the child. Children begin to be capricious, become lethargic, irritable, and complain of headaches and burning sensations in certain areas of the mucosa. However, an increase in temperature is not observed.
With a visual examination, small hyperemic spots can be found on the surface of the mucosa. The appearance of aft occurs in a few hours. As a rule, these are single erosions coated with fibrinous deposits. Within a week, such aphthae heal without leaving scars.
The nature of ulcers in aphthous stomatitis in adults is determined by the form of the manifestation of the disease:
- fibrinous. It is characterized by single rash on the mucous membrane of the lips, cheeks and tongue. In rare cases, localization of aphthae in areas of the gums and soft palate is possible;
- scarring. It is accompanied by the appearance of painful aphthae, prone to deepening and transition to ulcers. The places of localization of the rashes are the tissues of the salivary glands, the surface of the mucous membrane of the throat and palate. The epithelialization process is long and can take up to three months. As it heals, a whitish scar forms in the oral cavity at the site of the ulcer;
- necrotic. It manifests itself in dystrophic destruction of the epithelium, accompanied by mucosal necrosis. The resulting aphthae do not cause pain, but are prone to transition into ulcers. It is usually observed in patients with severe blood pathologies;
- glandular. It develops with damage to the tissues of the salivary glands. It is characterized by rashes in the area of small salivary glands. The healing period takes up to three weeks.
In the chronic course of aphthous stomatitis, the return of symptoms occurs from one (mild form) to six (severe form) once a year. In the complicated course of the disease, the occurrence of aft occurs continuously, and their number increases.
Methods for the treatment of aphthous stomatitis
The choice of a therapeutic technique for exposure to aphthous stomatitis depends on the specifics of the clinical picture and the presence of concomitant pathological processes.
The course of treatment of aphthous stomatitis provides an integrated approach using local and general therapy.
General therapy involves the use of funds aimed at strengthening the body as a whole - strengthening the protective potential, replenishing the deficiency of vitamins and minerals, normalizing the intestinal microflora, and reducing sensitivity to irritating or provoking factors.
Local exposure is the rehabilitation of the oral cavity and nasopharynx.
Use of medicines
The use of drug therapy is the best opportunity to provide quick and effective treatment of aphthous stomatitis.
Priority drugs are considered:
- immunomodulatory - Imudon, Kemantan, Diutsifon;
- antiviral - oxolinic ointment;
- antihistamines - Clemastine, loratadine;
- anesthetics - applications from lidocaine, trimecaine and pyromecaine;
- glucocorticoids - prednisone, clobetasol, dexamethasone;
- sedatives - valerian or motherwort extract, trioxazine;
- B vitamins
For the correction of cell metabolism, a complex effect is prescribed with drugs that stimulate metabolic processes. To remove fibrinous plaque, proteolytic enzymes are used.
Mouth rinse
An important component of local therapy for aphthous stomatitis are rinses. Thanks to this simple procedure, an antiseptic effect on the mucous membrane is carried out, the epithelization of the lesion sites is stimulated, and thus the healing of aphthous sites is accelerated.
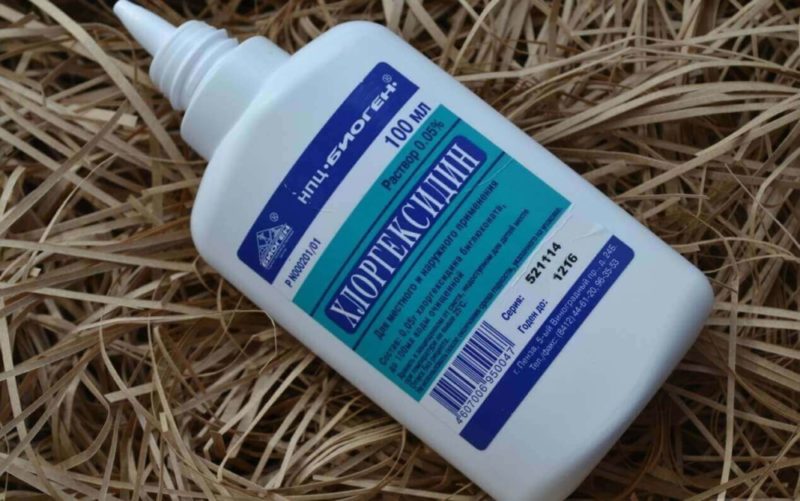
For rinsing, use a 0.2% solution of chlorhexidine, furatsilin or decamethoxin.
The use of Chlorhexidine involves three rinses with a small (10 ml) portion of the solution.
For rinsing with Furacilin, one tablet is used, dissolved in 100 ml of warm water. The procedure is performed six times a day.
Homeopathic remedies
The use of homeopathic remedies for aphthous stomatitis is justified not only by the absence of adverse reactions, but also by the effectiveness of the effect.
Among the most effective drugs recommended by homeopaths are Borax based on sodium boric acid, Kalium bichromicum, Natrium muriaticum and Arsenicum.
The use of these tools provides relief of inflammatory processes, stimulation of epithelization and accelerated healing of ulcers.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine methods suggest using grated potatoes for the treatment of aphthous stomatitis. A small amount of the potato mixture is kept in the mouth for several minutes. The procedure is repeated twice a day for a week.
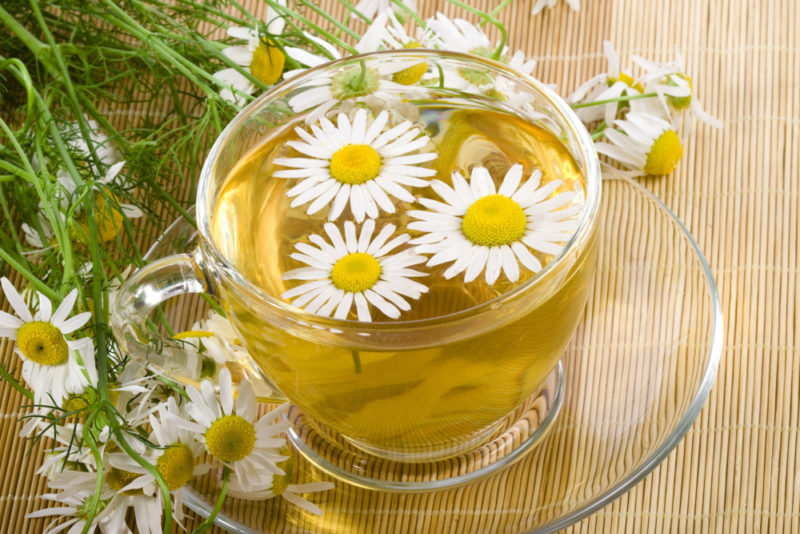
Another effective remedy is a decoction of pharmacy chamomile. This herb has unique anti-inflammatory properties and is able to speed up the healing process several times.
Chamomile is brewed, like regular tea, and used for rinsing. To enhance the healing effect, a little honey can be added to the decoction.
Diet for stomatitis
The organization of a properly balanced diet for stomatitis is the basis of a quick recovery. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, doctors recommend excluding from the menu products that can irritate the mucous membrane.
The diet therapy method provides for the temporary abandonment of such products:
- fruits - apples, plums, citrus fruits;
- sour vegetables and berries;
- spicy dishes, sauces, spices;
- pickles and pickles;
- • any solid products that can injure the mucous membranes.
Instead, nutritionists are advised to introduce into the diet soft and tender sour-milk products - cottage cheese, sour cream, yogurt, cheeses and milk porridge - oat, semolina, rice.
Instead of fried meat, it is better to cook boiled or baked. A broth with bay leaves will not only satisfy the hunger, but also provide additional healing effect.
In addition, with aphthous stomatitis, watermelons, melons and vitamin-rich juices from carrots, bell peppers or cabbage are useful.
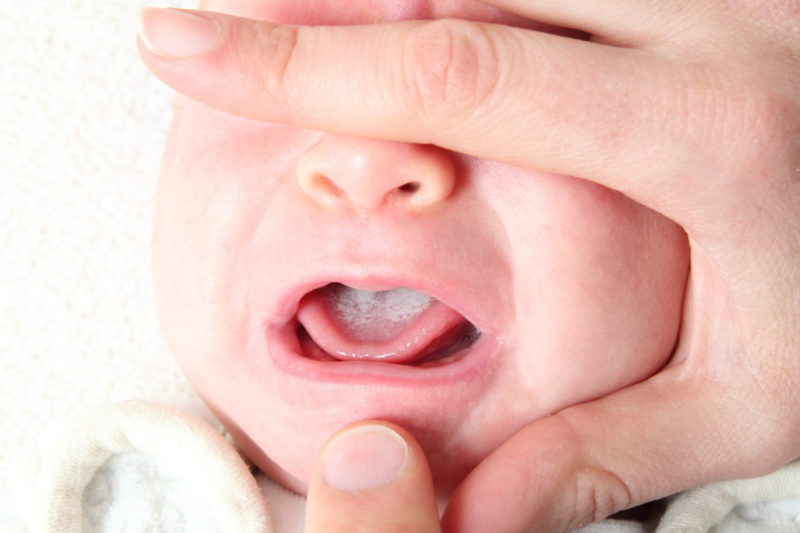
Features of the treatment of infants
The development of aphthous stomatitis can be observed in infants. The main thing is not to miss the onset of the disease and correctly establish the diagnosis, since the symptoms of the disease are often confused with the symptoms of a sore throat.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, infants are prescribed complex treatment aimed at strengthening the body's immune forces, eliminating the causes and symptoms of the disease. The choice of drugs is determined by the attending physician. Self-medication is not allowed.
Additionally, it is allowed to use traditional medicine methods - sea buckthorn oil or calendula tincture to lubricate erosion, tea with a pharmacy chamomile or blueberry.
In addition, it is necessary to provide hygienic procedures for the oral cavity of the baby.To treat the mucous membrane, decoctions of chamomile or sage, as well as solutions of potassium permanganate or furatsilina are used.
To avoid relapse, it is recommended to wash the toys with which the baby was in contact.
Preventative measures
The prognosis of aphthous stomatitis is generally favorable. However, a full recovery is possible only with timely diagnosis of a mild form of the disease and the provision of comprehensive treatment.
Prevention of aphthous stomatitis involves the elimination of provoking factors and the creation of optimal conditions for the formation of stable immunity.
A prerequisite for the prevention of aphthous stomatitis is a medical examination to identify gastrointestinal pathologies, endocrine system dysfunctions, as well as chronic infectious diseases with subsequent cure.
An important part of preventive measures are:
- dietary correction in favor of healthy foods rich in proteins and vitamins;
- compliance with the regime of the day
- uniform alternation of physical activity and rest;
- rejection of bad habits;
- personal hygiene support.
Compliance with the rules of prevention helps to avoid relapse even in the chronic form of the disease. And for healthy people - this is the best opportunity not only to improve health, but also to improve the quality of life.